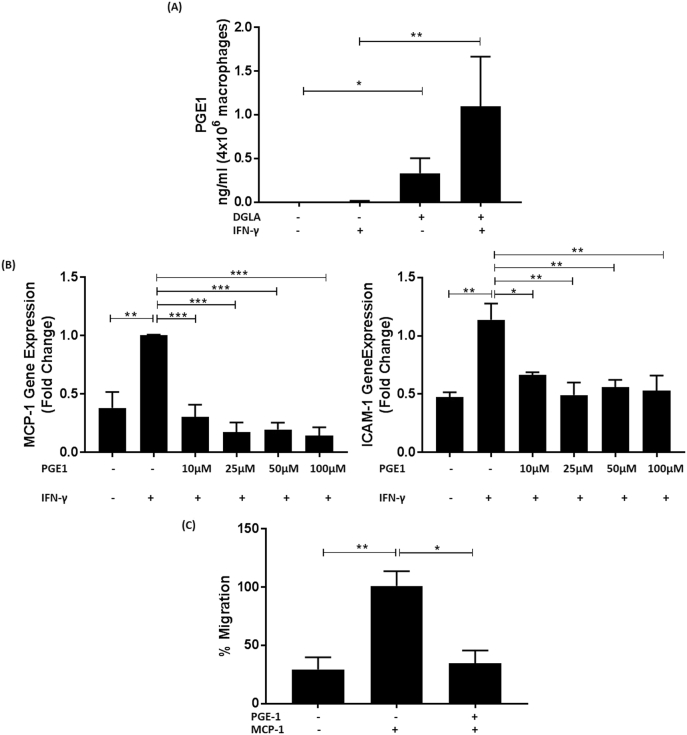
Fig. 8.
PGE1, a key metabolite of DGLA, inhibits macrophage pro-inflammatory gene expression and chemokine-driven monocytic migration.
(A), THP-1 macrophages were pre-incubated for 24 h with 100 μM DGLA (+) or vehicle (−) followed by a further 24 h stimulation with 250 U/ml IFN-γ (+) or its vehicle (−). Media was collected and lipids extracted for measurement using HPLC-MS. Graphs display concentration of PGE1 (ng/ml from 4 × 106 cells) from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM). (B), THP-1 macrophages were pre-incubated for 1 h with the indicated concentration of PGE1 (+) or DMSO vehicle (−). The cells were then treated for 3 h with 250 U/ml IFN-γ (+) or its vehicle (−). Total RNA was subjected to RT-qPCR using primers against MCP-1, ICAM-1 or GAPDH. The mRNA levels were calculated using the comparative Ct method and normalized to the housekeeping gene with values from cells pre-incubated with vehicle and then treated with IFN-γ given an arbitrary value of 1. Graphs display normalized gene expression (mean ± SEM) from three independent experiments. (C), migration assays were carried out with THP-1 monocytes incubated for 3 h with 10 μM PGE1 (+) or vehicle (−) using MCP-1 (20 ng/ml) as the chemoattractant. Cells incubated with vehicle in the absence MCP-1 were also included for comparative purposes. Monocyte migration was calculated by counting the number of cells that had migrated across a cell insert and expressed as a percentage of total input cells. Graph displays percentage migration (mean ± SEM), with MCP-1-driven migration in the presence of vehicle arbitrarily assigned as 100%. Statistical analysis was performed using a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post hoc test (A) or a One-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc analysis (B–C) (*, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001).