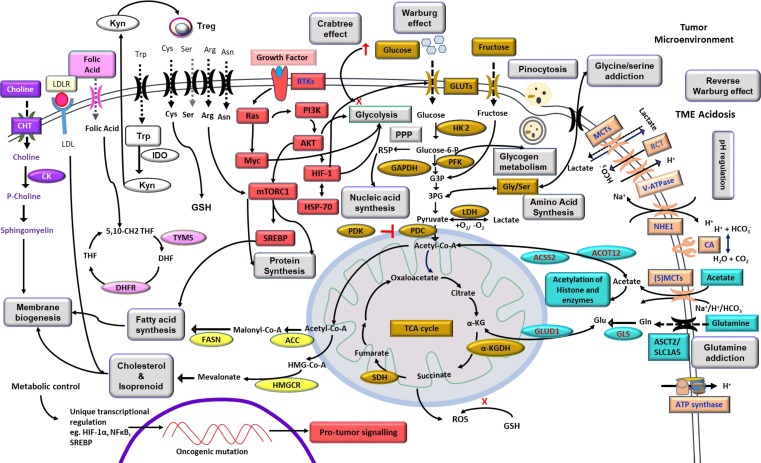
Figure 2.
Highlights of tumor metabolism. The diagram depicts metabolic reprogramming in tumor cells with overexpression of transporters meant for nutrient uptake, pH regulation, and receptors for cytokines, hormones, and other ligands. Internal components include prominent metabolic pathways of bioenergetics and biosynthetic machinery, including carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism, integration of metabolic networking for efficient utilization of substrates like glucose, fructose, lactate, acetate, amino acids, and precursor of membrane components. Signal transduction events indicate a crucial role of PI3K, HIF-1α, AKT, Ras, Myc, and mTOR downstream to receptor–ligand ligation with promoting consequences on metabolic pathways. The exterior of the membrane depicts a manifestation of the Warburg effect and modulation of the TME. Altered mitochondrial functions and its correlation to lipid metabolism, ROS generation, and glutamine assimilation are also depicted. The overall effect of such cross-talk of metabolic pathways resulted in the promotion of neoplastic cell survival. The diagram also indicates the metabolism-dependent regulation of gene expression. Carbohydrate metabolism is indicated by the golden color; cell signaling is indicated by the red color; alternative fuels and their cytoplasmic fates are indicated by the teal color; pH regulators are depicted by the orange color; choline metabolism is shown in purple color; enzymes of fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis are indicated by the yellow color; pink color represents folic acid metabolism; kynurenine and tryptophan pathways are depicted by the black and white boxes; amino acid transporters are shown in black; and major phenomena are indicated in boxes of gray color. Abbreviations: αKG, α-ketoglutarate; 3PG, 3phosphoglycerate; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACSS2, acyl-coenzyme A synthetase short-chain family member 2; ACOT12, acyl-CoA thioesterase 12; SLC1A5, neutral amino acid transporter B(0)/solute carrier family 1 member 5; CK, choline kinase; CHT, choline transporter; FASN, fatty acid synthase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3phosphate dehydrogenase; DHF, dihydrofolic acid; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; GLUD1, glutamate dehydrogenase 1; GLS, glutaminase; GLUT, glucose transporter; G3P, glucose-3-phosphate; HIF, hypoxia inducible factor; HK2, hexokinase 2; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3–methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A; HMGCR, HMG-CoA reductase; HSP-70, 70-kilodalton heat shock protein; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; Kyn, kynurenine; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; PDC, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; NHE1, Na+/H+ exchanger 1; PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; R5P, ribose-5phosphate; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Treg, regulatory T cells; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; THF, tetrahydrofolic acid; TYMS, thymidylate synthetase; (S)MCT, sodium-coupled monocarboxylate transporter; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding protein.