Fig. A1.
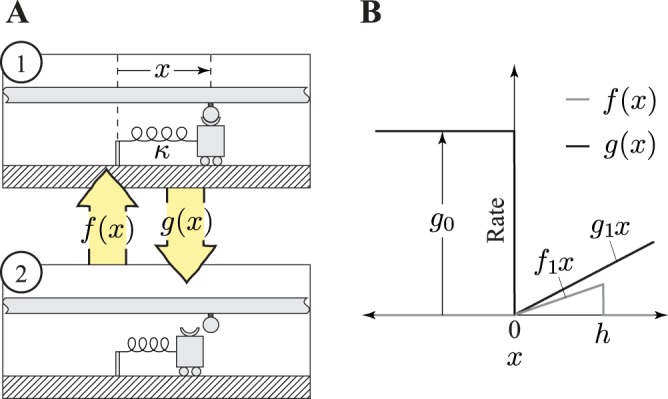
Kinetic scheme of the Huxley model. A: the Huxley model is a 2-state model; myosin is either attached to (1) or detached from (2) actin; x is the distance to a myosin-binding site on actin, and κ is the spring constant of the myosin head. The myosin-attached state shows the spring in the myosin head stretched out and generating force, whereas the detached myosin head does not generate force; f(x) is the attachment rate as a function of distance from the myosin binding site on actin, and g(x) is detachment rate. B: detachment and attachment rates as a function of distance from a myosin binding site. The parameters g1 and f1, are the slope of the detachment and attachment rates, respectively, as a function of positive x. Detachment rate assumes a constant value g0, and the attachment rate is zero when x is negative. The parameter h is the value of x at above which attachment can no longer occur. Lengthening a muscle will increase the x values of attached cross-bridges, whereas shortening decreases x.
