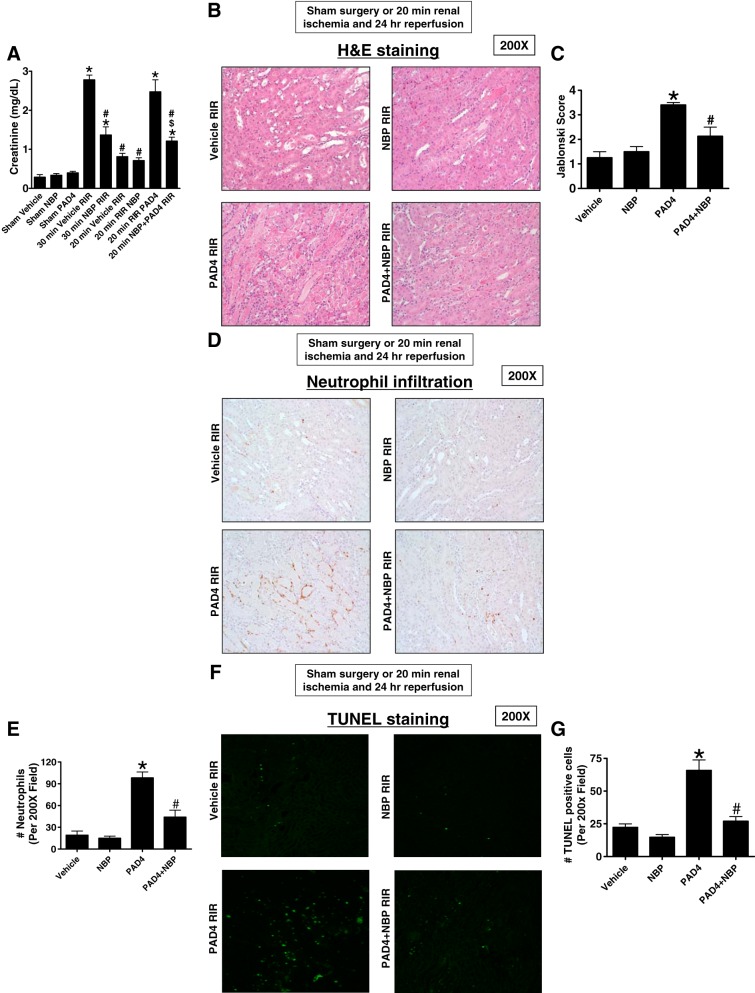
Fig. 5.
Ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) and peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 (PAD4)-mediated exacerbation of renal injury, neutrophil infiltration, and apoptosis is attenuated by NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) inhibition. A: mice subjected to 30-min renal ischemia-reperfusion (RIR) injury developed severe AKI with increased plasma creatinine. Mice treated with NEMO-binding peptide (NBP; 5 mg/kg iv 15 min before renal 30-min ischemia) were protected against 30-min RIR injury with reduced plasma creatinine. Recombinant PAD4 treatment (10 μg iv 15 min before renal ischemia) exacerbated injury in mice subjected to 20-min RIR. NBP given 15 min before PAD4 prevented the PAD4-mediated exacerbation of ischemic AKI in mice (n = 4–6). *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle-sham; #P < 0.05 vs. vehicle 30-min RIR; $P < 0.05 vs. PAD4 20-min RIR. Error bars = 1 SE. B and C: representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained images (from 4−6 experiments; B) and renal injury scores (C) assessing the degree of renal tubular necrosis (scale of 0–4; Ref. 32) of mice subjected to 20-min renal ischemia and 24-h reperfusion (magnification: ×200). The kidneys of mice treated with recombinant PAD4 (10 μg iv 15 min before renal ischemia) and subjected to RIR showed increased tubular necrosis and proteinaceous casts as well as increased tubular dilatation and congestion compared with vehicle-treated mice. Mice treated with NBP 15 min before PAD4 treatment had significantly decreased renal tubular necrosis, congestion, and cast formation. D and E: representative images (from 4−6 experiments; D) of immunohistochemistry for neutrophils (dark brown) and counts of infiltrating kidney neutrophils (E; n = 4–6) in the kidneys in the kidneys of mice subjected to 20-min renal ischemia and 24-h reperfusion (magnification: ×200). Neutrophil infiltration markedly increased in mice treated with recombinant PAD4 at 10 μg iv 15 min before renal ischemia (concentrated near the corticomedullary junction). Mice treated with NBP 15 min before PAD4 treatment had significantly decreased neutrophil infiltration. F and G: representative images of TUNEL staining indicative of renal tubular apoptosis (F) and counts of TUNEL-positive kidney cells (G; n = 4). Increased renal tubule cell apoptosis occurred in mice treated with recombinant PAD4 at 10 μg iv 15 min before 20-min RIR injury. Mice treated with NBP 15 min before PAD4 treatment had significantly decreased TUNEL-positive renal tubule cells 24 h after reperfusion.