Fig. 7.
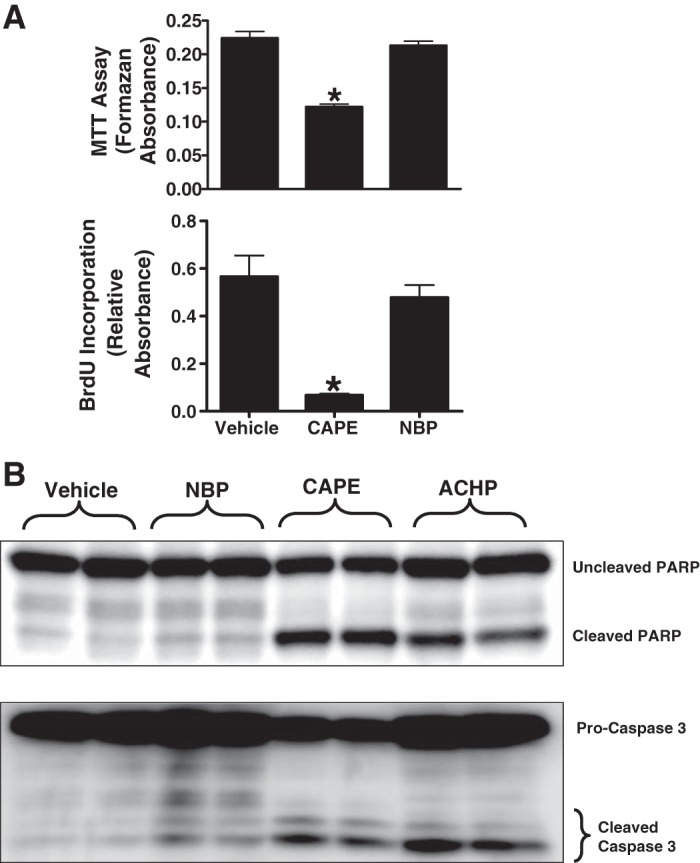
NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) blockade does not affect renal tubular cell proliferation, survival, or promote apoptosis. HK-2 cells were treated with one of the NF-κB signaling inhibitors {10 μM NEMO-binding peptide (NBP; selective IKKγ inhibitor), 25 μg/ml caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE; selective NF-κB inhibitor), or 10 μg/ml 2-amino-6-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)-6-hydroxyphenyl]-4-(4-piperidinyl)-3-pyridinecarbonitrile (ACHP; selective IKKα and IKKβ inhibitor)} or with vehicle (1% DMSO) for 16 h. A: NF-κB inhibition with CAPE significantly reduced HK-2 cell survival (MTT assay, n = 4; top) and proliferation [bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation into DNA, n = 4; bottom]. B: NF-κB inhibition with either ACHP or CAPE significantly increased apoptosis [caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) fragmentation, n = 4]. In contrast, selective IKKγ inhibition with NBP treatment did not significantly attenuate cell proliferation, survival, or induce apoptosis in HK-2 cells. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle.
