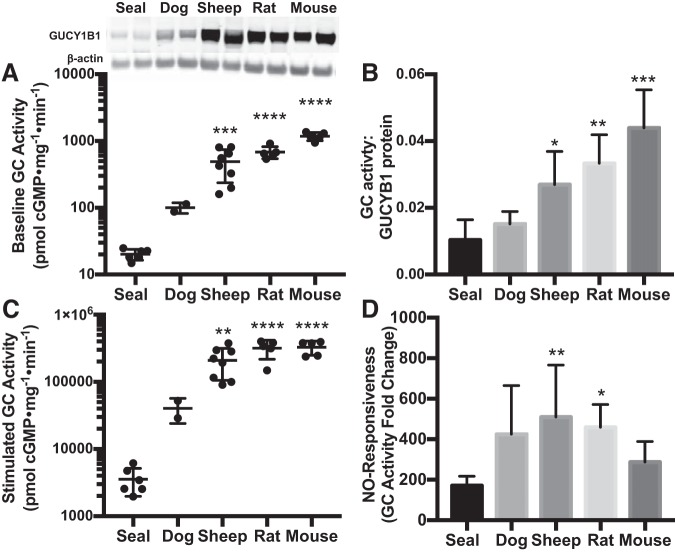
Fig. 2.
Guanylyl cyclase (GC, GUCY) activity in adult lung is lower in seals than in terrestrial mammals. A: baseline GC activity in lung is lower in seal (n = 6) than in dog (n = 2), sheep (n = 8), rat (n = 5), and mouse (n = 5). Inset: protein content of the GC β-subunit (GUCY1B1, 70-kDa band) was also lowest in seal lung. B: after baseline GC activity to GC protein level was normalized, enzyme activity per unit protein remains higher in lungs of mice, rats, and sheep than in Weddell seals. C: GC activity stimulated with an in vitro nitric oxide (NO) donor is also lowest in seals. D: stimulated GC activity relative to baseline indicates the capacity for NO to stimulate GC (NO responsiveness), which is also lower in seal lungs than in sheep or rats. Error bars represent means ± SD. Asterisks denote significant differences from adult seals by Sidak post hoc pairwise comparisons following an overall species difference detected by ANOVA (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).