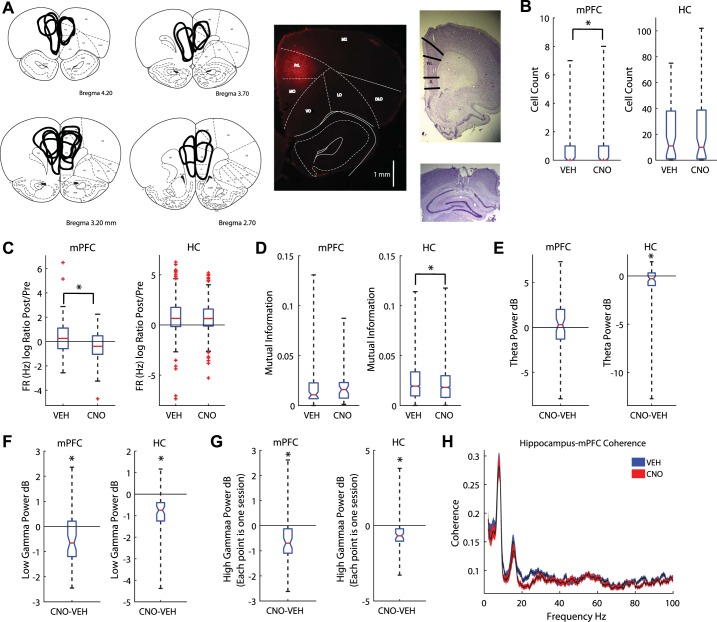
Fig. 1.
Clozapine N-oxide (CNO) altered medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and hippocampal local field potentials. A: the mPFC was transduced with the designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs) AAV8-CaMKIIa-hM4Di. Summary figure of DREADDs spread (left) and example photo of fluorescence (middle). Tetrodes were targeted toward CA1 (cornu ammonis, bottom right) and the prelimbic cortex of the mPFC (top right). B: CNO reduced the number of cells recorded in the mPFC (left) but had no effect on recordings in the hippocampus [HC; boxplot: median is plotted (red line), whiskers extend to outliers]. C: CNO decreased the firing rate (FR) ratio between premaze rest (Pre) and postmaze rest (Post) in the mPFC (left); it had no effect on hippocampal cells (right). D: we measured the mutual information (MI) between spatial location and spike firing (see methods). CNO had no effect on the MI for neurons in the mPFC (left). However, CNO decreased place cell MI (right). E: we measured the differences in theta power between CNO and vehicle (Veh) days. mPFC disruption did not alter theta power in the mPFC (left) but did reduce it in the hippocampus (right). The median difference between Veh and CNO theta power is plotted for all rats. F: we found a decrease in low gamma power in both the mPFC (left) and hippocampus (right). G: high gamma power also decreased in the mPFC (left) and hippocampus (right). H: coherence plot between the hippocampal and mPFC local field potentials. Blue, Veh; red, CNO. Values are means ± SE. dB, decibels; DLO, dorsolateral orbital cortex; IL, infralimbic cortex; LO, lateral orbital cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex; MO, medial orbital cortex; RrL, prelimbic cortex; VO, ventral orbital cortex. *P < 0.05.