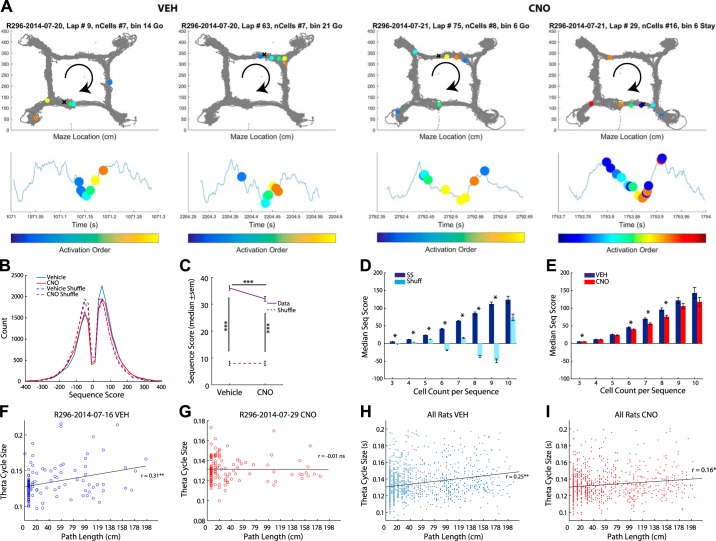
Fig. 5.
Disrupting the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) with designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs) altered hippocampal theta sequences. A: examples of sequences (top row) for vehicle (Veh) (left) and clozapine N-oxide (CNO; right) days. Each panel represents a theta sequence. The gray dots represent all trajectories taken. The colored dots represent the place cell location best represented in the sequence. The “x” marks the location of the rat on the maze. The change in color represents cell order in the firing sequence. The same cell firing order (represented in the same colors as the top panel) are plotted along the theta sequence (bottom). B: we measured the sequence score, the coherent sequence of place cell activity, of individual theta cycles for Veh and CNO days (Gupta et al. 2010, 2012; see methods). As a control we calculated the sequence scores of the same data set with the spiking ordered shuffled (see methods for shuffling procedure). C: sequence scores were significantly different from zero. Sequence scores were smaller for CNO days. The real data were significantly different from the shuffled data. The shuffled data, however, were not significantly different from zero or each other. D: larger ensemble sizes do not necessarily produce larger sequence (Seq) scores. We measured the median sequence score for ensembles ranging from 3 to 10 cells for Veh data (dark blue) and shuffled Veh data (light blue). E: examining the median sequence score across different ensemble sizes reveals that CNO (red) theta cycles consistently had lower sequence scores than Veh (dark blue) theta cycles. F and G: examples of correlation between the length of the theta cycle measured against the Bayesian decoded path length for a Veh (F) and CNO (G) day. H: the size of the theta cycle positively correlated with the Bayesian decoded path length on Veh days (I) and CNO days; however, this relationship was significantly reduced in CNO days compared with Veh days. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.