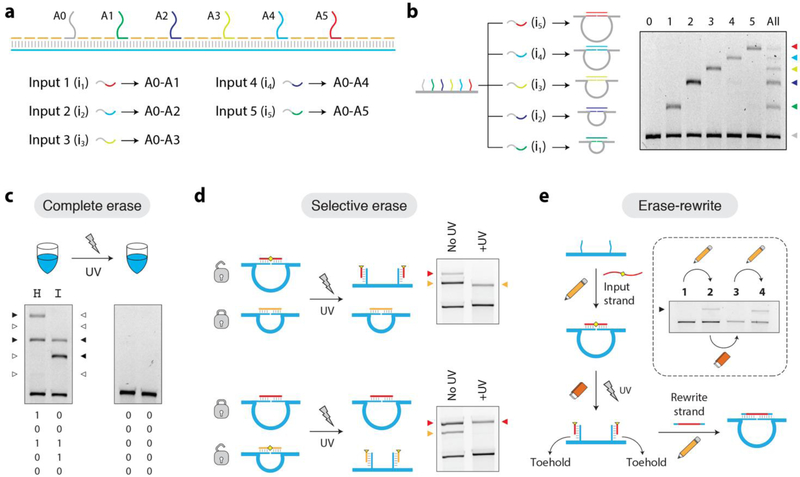
Figure 3. Multi-input DNA nanoswitches and photo-response.
(a) A nanoswitch containing six address sites (A0–A5) that can recognize five different targets. (b) All target strands can bind to A0, but the second half binds to different address sites (0–1, 0–2, 0–3, 0–4, 0–5), leading to loops of different sizes that migrate differently on an agarose gel. (c) The word “HI” encoded using the 5-bit Baudot code by triggering different loops of the nanoswitch. The written information can be erased using UV. (d) Loops formed by PCL-containing inputs can be specifically erased among others. (e) Information (looped bits) erased using UV can be re-written using longer input strands through strand displacement.