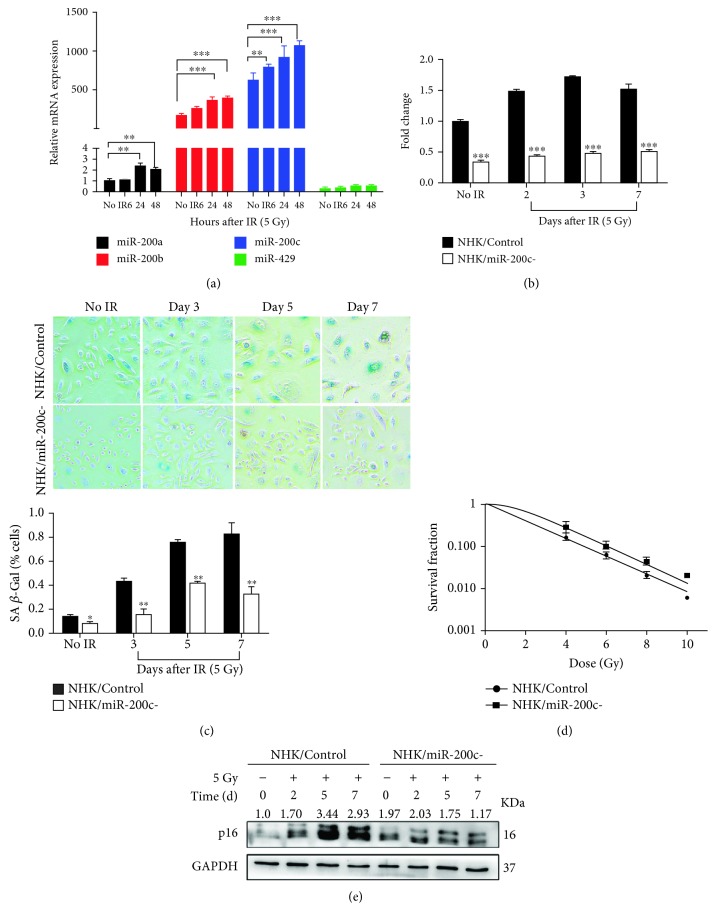
Figure 2.
miR-200c modulates proliferation and senescence in NHKs exposed to IR. (a) The expression level of miR-200 family was measured by qPCR (mean ± S.D.) at indicated time after being exposed to 5 Gy. 5S rRNA was used as an internal control. ∗∗ P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗ P < 0.001 vs. nonirradiated cells. (b) NHKs were infected with sh-miR-200c (NHK/miR-200c-) or a scrambled negative control (NHK/Control); miR-200c expression was measured by qPCR (mean ± S.D.) at days 2, 3, and 7 after being exposed to 5 Gy. 5S rRNA was used as an internal control. ∗∗∗ P < 0.001 vs. NHK/Control. (c) SA-β-Gal assay was performed in NHK/Control and NHK/miR-200c- cells at days 0, 3, 5, and 7 postirradiation; the numbers of positive cells were counted (mean ± S.D.). IR-induced senescent cells were much less in NHK/miR-200c- compared with NHK/Control cells. ∗ P < 0.05 and ∗∗ P < 0.01 vs. NHK/Control. Scale bar 200 μm. (d) NHK/Control and NHK/miR-200c- cells were cultured in 6-well plates for 24 hours before being irradiated with the indicated doses. Cells were further cultured for 10 days, then the colonies were counted; surviving fractions were determined by the number of colonies divided by the number of seeded cells × plating efficiency. (e) Western blotting was performed for p16INK4A and GAPDH (internal control) in NHK/Control and NHK/miR-200c- cells at indicated time after being exposed to 5 Gy.