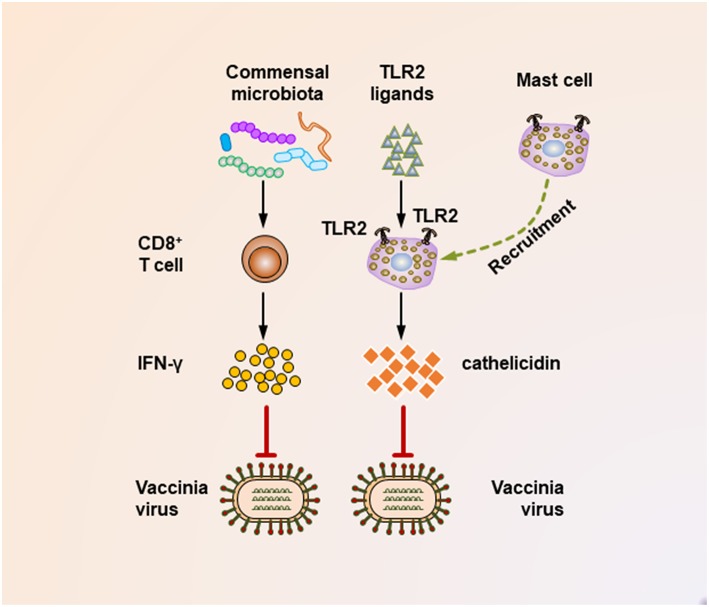
Figure 2.
Mechanisms underlying the suppression of vaccinia virus infection by the commensal microbiota. During the vaccinia virus infection, the commensal microbiota primes virus-specific CD8+ T cells to secrete large amounts of IFN-γ, which critically mediates the corresponding antiviral immunity. In addition, during vaccinia virus infections, the activation of TLR2 by bacterial products is essential for recruiting mast cells to sites of viral infection. These mast cells also contribute to suppressing the viral infection by secreting an antiviral cathelicidin.