Figure 2.
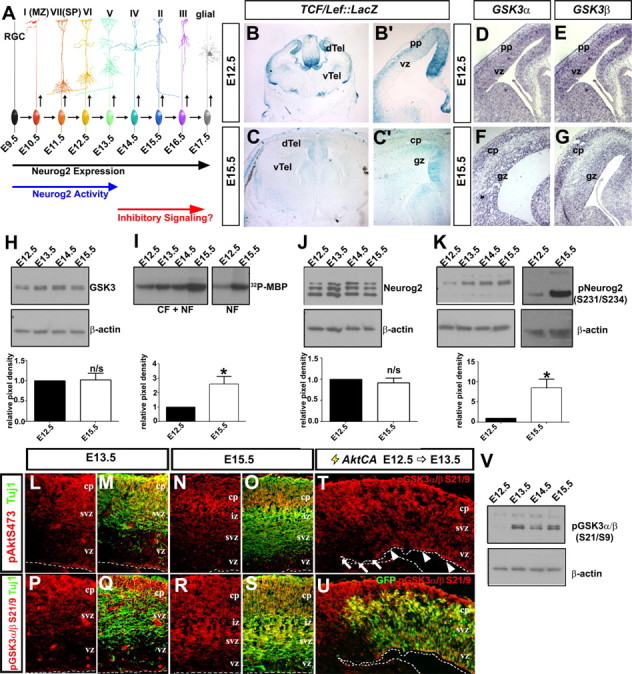
Temporal change in GSK3β kinase activity and Neurog2 phosphorylation during neocortical development. A, Extrinsic model of posttranscriptional inactivation of Neurog2 during late stages of neocortical development. B, C, β-Galactosidase histochemical stain of E12.5 (B, B′) and E15.5 (C, C′) TCF/Lef-LacZ transgenic cortices. D–G, Distribution of GSK3α (D, F) and GSK3β (E, G) transcripts in E12.5 (D, E) and E15.5 (F, G) neocortices. H, Expression analysis of GSK3 protein from E12.5 to E15.5 neocortical lysates normalized against β-actin (loading control) protein levels. I, GSK3β kinase activity, assayed via P-32 phosphorylation of a myelin basic protein substrate by GSK3β immunoprecipitated from E12.5 to E15.5 neocortical cellular fraction (CF) or nuclear fraction (NF) protein extracts. J, K, Western blot analysis of total Neurog2 (J) or pNeurog2 (S231/234; K) expression from E12.5 to E15.5, normalized against β-actin (loading control). L–S, Coexpression of pAkt (S473, red) and Tuj1 (green) (L–O) and pGSK3α/β (S21/9, red) and Tuj1 (green) (P–S) in E13.5 and E15.5 neocortical sections. T, U, E12.5→E13.5 electroporation of AktCA promotes phosphorylation of GSK3α/β (S21/9) in GFP+ VZ progenitors (arrowheads), but not in adjacent GFP− cells (arrows). V, Western blot analysis of GSK3α/β (S21/9) in E12.5 to E15.5 cortical lysates. The asterisk (*) indicates significantly different, p < 0.05. Error bars indicate SEM. cp, Cortical plate; dTel, dorsal telencephalon; gz, germinal zone; pp, preplate; svz, subventricular zone; vTel, ventral telencephalon; vz, ventricular zone.
