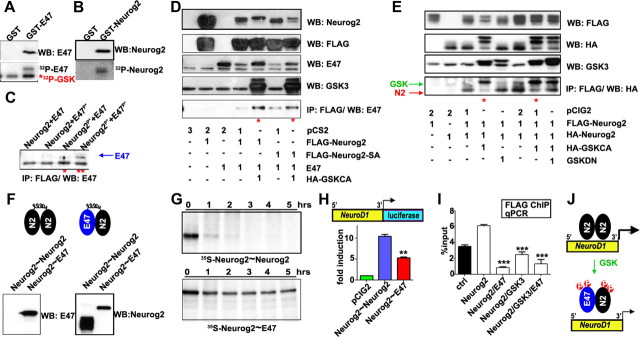
Figure 7.
GSK3β regulates Neurog2 cofactor associations. A, B, P-32 phosphorylation of purified GST-E47 or GST-Neurog2, by GSK3β in vitro. C, Western blot of in vitro-transcribed/translated E47 coimmunoprecipitated with FLAG-Neurog2, after additional P-32 phosphorylation by GSK3β as indicated. The blue arrow indicates specific band. D, Assessment of the association between E47 and FLAG-Neurog2 via coimmunoprecipitation from cell extracts cotransfected with combinations of pCS2 (empty vector control), FLAG-Neurog2, FLAG-Neurog2-SA (S231/234A), E47, or HA-GSKCA as indicated. The red asterisks denote enhanced association. E, Assessment of Neurog2 dimerization via coimmunoprecipitation of HA-Neurog2 with FLAG-Neurog2 from cell extracts cotransfected with combinations of pCIG2 (empty vector control), FLAG-Neurog2, HA-Neurog2, HA-GSKCA, or GSKDN as indicated. The red asterisks denote decreased association. The red and green arrows indicate the specific bands for Neurog2 and GSK3β, respectively. F, Western analysis of tethered Neurog2∼Neurog2 or Neurog2∼E47 forced dimer constructs. G, Degradation time course of in vitro-transcribed/translated, S35-labeled forced dimer constructs. H, Comparison of Neurod1 promoter transactivation by forced dimer constructs. I, Analysis of FLAG-Neurog2 occupancy on the Neurod1 promoter when coexpressed with combinations of E47 or GSK3 constructs as indicated. J, Model of GSK3-mediated suppression of Neurog2 by phosphorylation-induced cofactor association. The p values are denoted as follows: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. Error bars indicate SEM.