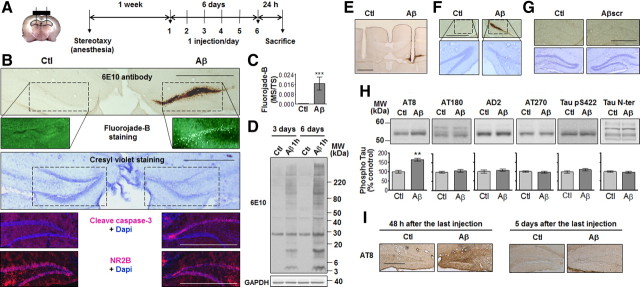
Figure 2.
Neuronal deaths induced by Aβ1–42-oligomer deposition and tau phosphorylation following repeated intrahippocampal injections. A, Bilateral cannulae were stereotaxically implanted in the DG. One week following surgery, Aβ1–42 oligomers (Aβ; 0.2 μg/μl; 2 μl) and vehicle (Ctl) were simultaneously injected collaterally in awake, freely moving mice once a day for 6 consecutive days and killed 24 h following the last injection. B, Representative accumulation of Aβ1–42 oligomers in the DG on a section immediately next to the cannulae insertion site. Bottom, Representative staining with Fluoro-Jade B, cresyl violet, cleaved caspase-3 antibody, and NR2B antibody. C, Quantification of Fluoro-Jade B staining within the DG 24 h following the last injection. Marked surface (MS) versus total surface (TS) counted (n = 4, ***p < 0.001). D, Representative immunoblots of Aβ1–42 oligomer profiles 24 h following the last injection. E, Representative 6E10-immunostained section showing cannulae insertion. F, Representative accumulation of Aβ1–42 oligomers and cell death when the Aβ1–42 preparation is injected in the more ventral part of the hippocampus (−3.4 mm AP, ±2.0 mm ML, −2.4 mm DV from bregma) in sections stained with the 6E10 antibody and cresyl violet. G, Representative DG sections stained with 6E10 antibody and cresyl violet following collateral injections (1 per day for 6 d) of vehicle (Ctl) and scrambled Aβ1–42 (Aβscr; 0.2 μg/μl; 2 μl). H, Representative immunoblots of tau phosphorylation in the dorsal hippocampus of mice injected collaterally with vehicle (Ctl) and Aβ1–42 oligomers for 6 d. Bottom, Densitometric quantification of changes expressed as the mean ratio of phospho-tau to total tau antibody (Tau N-ter) staining. Error bars indicate ± SEM. **p < 0.01. I, Representative AT8-immunostained section 24 h and 5 d after the last injection (n = 4, two independent experiments). Scale bars: 50 μm.