Figure 7.
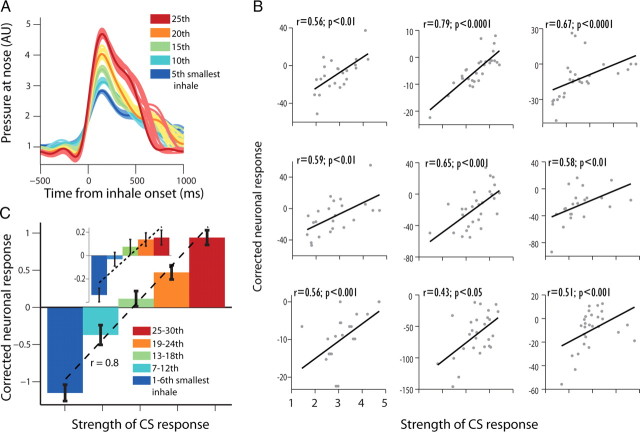
Preparatory neural responses indicate trial-by-trial learning. A, We matched 10 spontaneous inhales with the minimal Euclidian distance to each single-trial CR (preparatory behavioral response). Shown are five different CRs (solid line of 5 different sizes for easier presentation) from one session overlaid with their matched spontaneous controls (thin line shaded color). Neural responses from these controls were used to correct the neural response for the CS on a trial-by-trial basis, hence removing the portion of the response that belongs to the behavior per se (e.g., motor-inhale). B, trial-by-trial correlations of behavioral response (CR) with corrected CS-evoked neural response for 9 neurons (Spearman-correlation and p values are shown on top). C, CRs from all trials and sessions were pooled to five bins according to relative size, and correlated with neural responses averaged across all cells with positive correlation. This revealed a significant relationship (r = 0.8, p < 0.001, Pearson) between neuronal response and learning that is independent of the pure behavioral response. The relationship is significant also when using all available cells (inset, r = 0.18, p < 0.01).