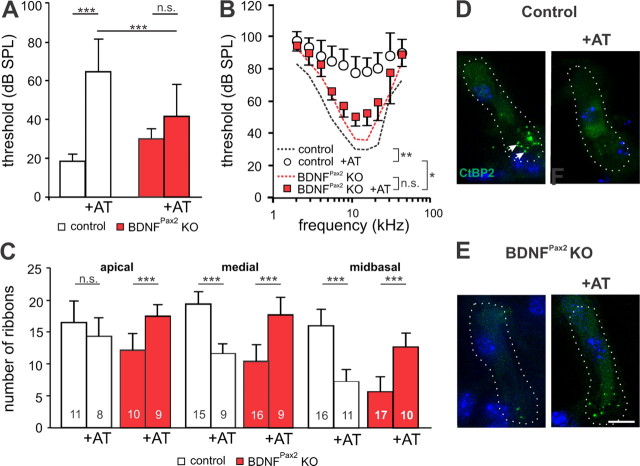
Figure 5.
BDNFPax2 KO mice are less vulnerable to noise trauma. A, B, Mean ABR thresholds ± SD for click stimuli (A) and mean frequency-specific ABR thresholds ± SD (B), seven days after noise exposure (AT, 116 dB SPL, 10 kHz, for 40 min) in control and BDNFPax2 KO mice (nonexposed control: n = 6/12 mice/ears; control +AT: n = 8/16; nonexposed BDNFPax2 KO: n = 6/12, BDNFPax2 KO +AT: n = 8/16; A, one-way ANOVA: p < 0.001; B, two-way ANOVA: p < 0.001). C, Ribbon counts from three different frequency cochlear regions in sham- or noise-exposed controls and BDNFPax2 KO mice (one-way ANOVA: p < 0.001); n = 3 mice. Numbers of IHCs counted are given in the bars. D, E, Immunohistochemistry for CtBP2/RIBEYE (green) in controls (D) and BDNFPax2 KO mice (E) before and 14 d after noise exposure (+AT), shown for the midbasal turn. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI; scale bar, 10 μm. n = 3 mice, done in triplicate.