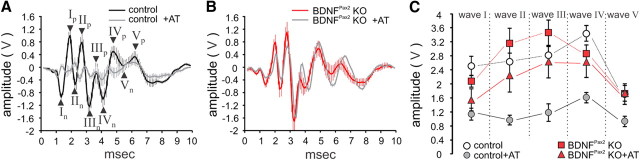
Figure 6.
Peak-to-peak amplitudes of ABR waves are not reduced in BDNFPax2 KO mice following noise exposure. ABR waves illustrate the difference in signal amplitude in control (A) and BDNFPax2 KO mice (B) before and 7 d after trauma (AT; ±SEM), shown for stimulation with clicks presented at 20 dB above the hearing threshold. C, Peak to peak amplitudes at 20 dB above hearing threshold for five selected peak-to-peak amplitudes (wave I-V, arrows in D, two-way ANOVA: p < 0.001). After exposure the amplitude of control mice was significantly reduced for waves II-V compared with pre-exposure (two-way ANOVA: p < 0.05). Amplitudes of BDNFPax2 KO mice were not significantly decreased after exposure. Control, n = 8/16 mice/ears; BDNFPax2 KO, n = 8/16.