Figure 2.
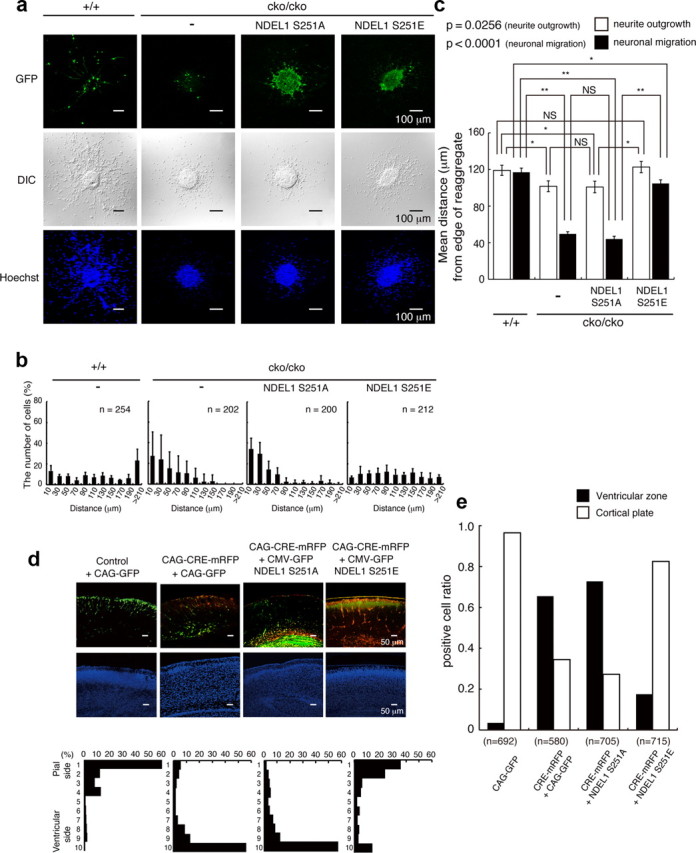
Defective migration of Ndel1 hypomorphic mutant and rescue experiments. a, Migration assay using cerebellar granule neurons after transfection of Control GFP, GFP-Ndel1 (S251A), or GFP-Ndel1 (S251E). GFP images (top), differential interference contrast (DIC) images (middle), and Hoechst staining images (bottom) are shown. Ndel1cko/cko neurons displayed defective migration. b, The migration distance of each neuron 48 h after the start of culture was binned. n is the number of neurons measured for each examination. Wild-type neurons displayed normal migration distances, whereas Ndel1cko/cko neurons displayed a shift in the distribution of bins toward the left. Expression of GFP-Ndel1 (S251A) had no effect on migration of Ndel1cko/cko neurons, whereas expression of GFP-Ndel1 (S251E) significantly improved migration of these neurons. c, Mean length of neurites (open bar) and nuclear position (solid bar) from the edge of central aggregation. Note: Granular neurons from Ndel1cko/cko mice displayed reduced neurite extension and nuclear migration. Reduction of nuclear migration appeared to be disproportionally more severe than impaired neurite extension. NDEL1 (S251E) efficiently rescued impaired extension of the leading processes and defective neural migration. Statistical analysis was performed for neurite outgrowth and nuclear migration by an ANOVA followed by t test with correction: *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. Error bars in graphs represent mean ± SEM. d, In utero injection of mRFP-Cre, control GFP, GFP-Ndel1 (S251A), or GFP-Ndel1 (S251E) into the E16.5 mouse neocortex of Ndel1cko/cko embryos by electroporation. GFP or mRFP/GFP images are shown in the top panels. Counterstains of a neighboring section by DAPI are displayed in middle panels. The distribution of migrated neurons are shown in the bottom panels. The cortex was divided into 10 bins, and the numbers of neurons were counted in each bin. GFP or mRFP/GFP images of cryosections are representative of six different pups from two independent in utero injections. In the control, GFP-positive neurons moved into surface area of the cortex (first lane). By contrast, disruption of Ndel1 by CRE recombinase severely impaired upward localization of cortical neurons (second lane), and this defective localization was efficiently rescued by cotransfection of GFP-Ndel1 (S251E: fourth lane) but not by GFP-Ndel1 (S251A: third lane). e, Distribution of mRFP-CRE/GFP-expressing cells within the brain. A fraction of mRFP-CRE/GFP-expressing cells remained within the ventricular zone after disruption of Ndel1. Expression of GFP-NDEL1(S251E) rescued these phenotypes. The total numbers of counted cells are indicated.
