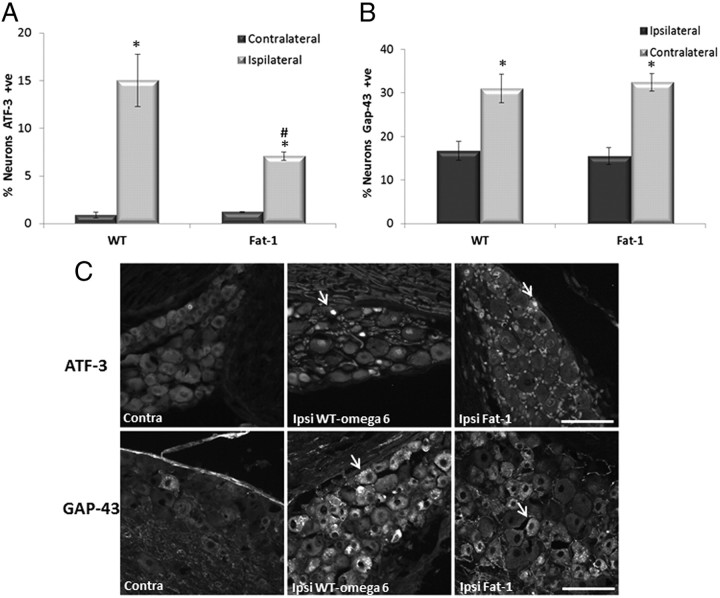
Figure 5.
ATF-3 and GAP-43 expression in DRG neurons 7 d after sciatic nerve injury. Immunoreactivity for ATF-3 (A) and GAP-43 (B) was analyzed in L4 and L5 DRG neurons removed 7 d after sciatic nerve crush. C, Example of neurons positive for ATF-3 and GAP-43 are marked with a yellow arrow. Scale bar, 100 μm. ATF-3 and GAP-43 staining detected in lumbar DRG neurons contralateral (Contra) to nerve injury was low. Both ATF-3 and GAP-43 staining was seen in a high proportion of cells in the ipsilateral (Ipsi) DRG after injury (*p < 0.05). There was a significant difference between WT ω-6 and fat-1 in the percentage of neurons expressing ATF-3 after injury, with a smaller percentage of ATF-3 neurons in fat-1 mice (#p < 0.05) (means ± SEM, n = 11 animals per group).