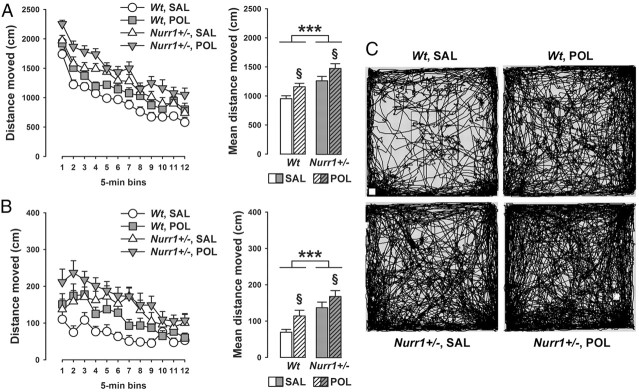
Figure 2.
Additive effects between prenatal immune activation and Nurr1 deficiency in the development of spontaneous locomotor hyperactivity. Pregnant wt and Nurr1+/− mice were treated with the viral mimetic poly(I:C) (POL) (2 mg/kg, i.v.) or vehicle [saline (SAL)] on gestation day 17, and the resulting offspring were tested in early adulthood. A, The line plot depicts the total distance moved in the entire open field area as a function of 5 min bins, and the bar plot shows the mean distance moved across the 1 h test period. ***p < 0.001 and §p < 0.01, signifying the main effects of genotype and prenatal treatment, respectively. N = 14 in each experimental group; all values are means ± SEM. B, The line plot represents the distance moved in the center zone of the open field as a function of 5 min bins, and the bar plot depicts the mean center zone distance moved across the 1 h test period. ***p < 0.001 and §p < 0.01, signifying the main effects of genotype and prenatal treatment, respectively. N = 14 in each experimental group; all values are means ± SEM. C, Computer-generated path drawings of representative SAL- or POL-exposed wt and Nurr1+/− offspring in the open-field test.