Figure 8.
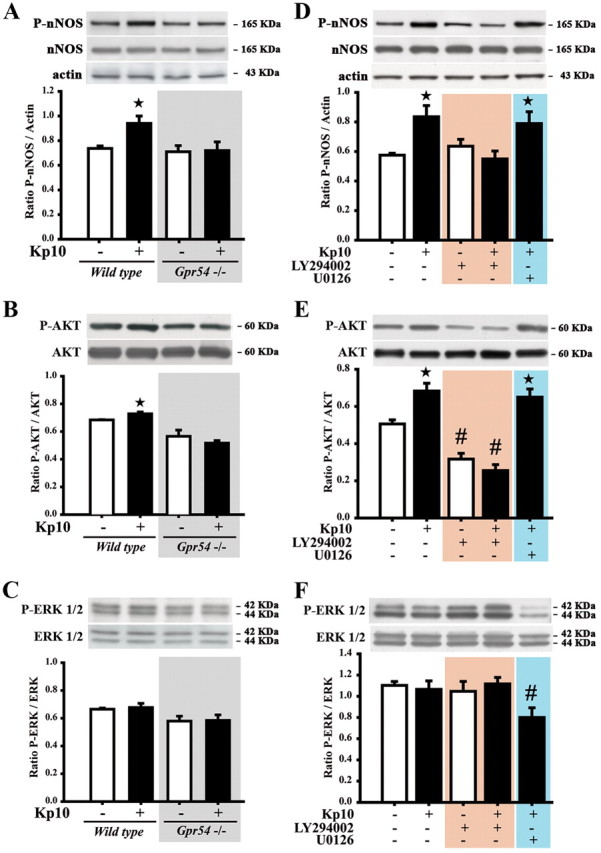
The activation of the GPR54 and PI3K-AKT pathways are necessary for the kisspeptin-induced increase in nNOS phosphorylation. A–F, Representative immunoblots showing that kisspeptin promotes nNOS (A, D) and AKT (B, E), but not ERK (C, F) phosphorylation in a GPR54-dependent manner (A, B) in diestrous (A–C) and ovariectomized (D–F) mice; the effects of kisspeptin are inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 but not the MEK inhibitor U0126 (D–F). Bar graphs illustrate the mean ratio of the signal obtained for P-nNOS to that of actin (D), the ratio of P-AKT to that of AKT (E), and of P-ERK and that of ERK (F) from four independent experiments. Error bars indicate SEM. * and #, p < 0.05, experimental groups versus untreated controls.
