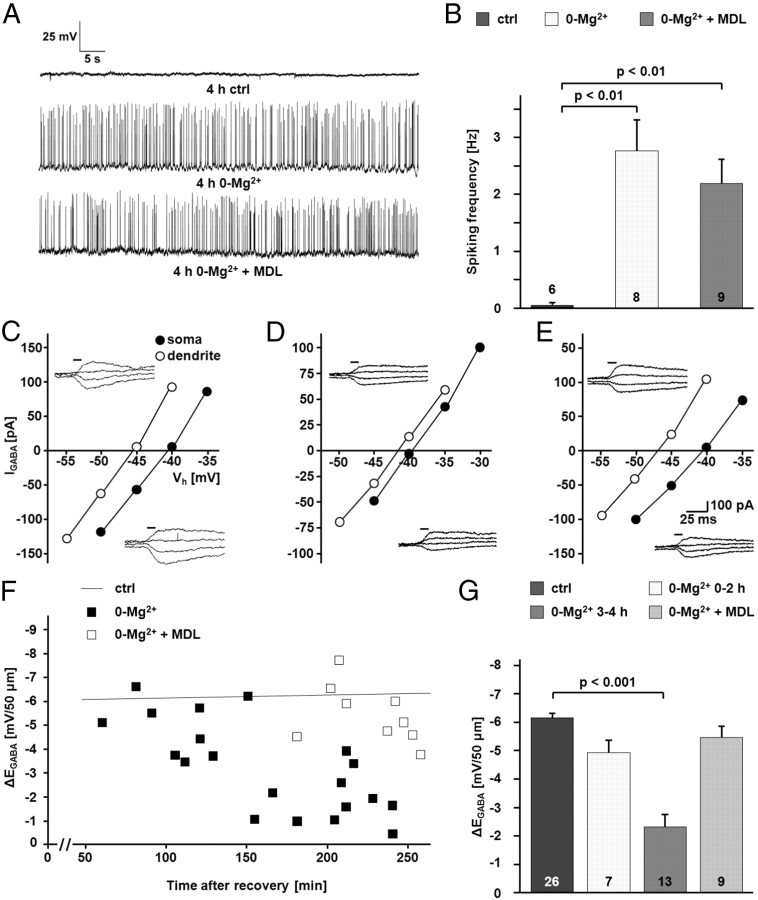
Figure 5.
Interictal-like activity leads to a calpain-dependent functional inactivation of KCC2. A, Current–clamp recordings illustrating an increase in neuronal activity in CA1 pyramidal cells induced by the incubation of hippocampal slices in Mg2+-free physiological solution. The increase in activity was not blocked by the calpain inhibitor MDL-28170. B, Quantification of the current–clamp recordings. The increase in the spiking frequency in Mg2+-free physiological solution was significant (2.77 ± 0.57 Hz vs 0.032 ± 0.03 Hz for 0-Mg2+ and control (ctrl), respectively; p < 0.01). The increase in frequency took also place when MDL-28170 (MDL) was present in the physiological solution (2.2 ± 0.43 Hz; not significantly different when compared to 0-Mg2+ and p < 0.01 when compared to control). C–E, Sample recordings of uncaging-induced IGABA at the soma and at a distance of 50 μm in the apical dendrite. I–V curves are based on IGABA at different holding potentials (Vh) under control conditions (C), in Mg2+-free physiological solution (D), and in Mg2+-free physiological solution in the presence of MDL-28170 (E). F, Scatter plot of ΔEGABA over time in neurons kept in Mg2+-free physiological solution with or without MDL-28170. For comparison, the line representing the linear fit for the control cells shown in Figure 2 is included. G, Quantification of ΔEGABA revealed a MDL-28170-sensitive decrease in the Cl− extrusion in neurons from slices incubated in Mg2+-free physiological solution (0-Mg2+: −2.33 ± 1.62 mV/50 μm; MDL-28170: 5.44 ± 0.40 mV/50 μm; p < 0.001). The pooled control data shown in Figure 2 are included for comparison. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with Scheffe's post hoc test. The values for n are given in the bar diagram. Error bars denote SEM.