Figure 2.
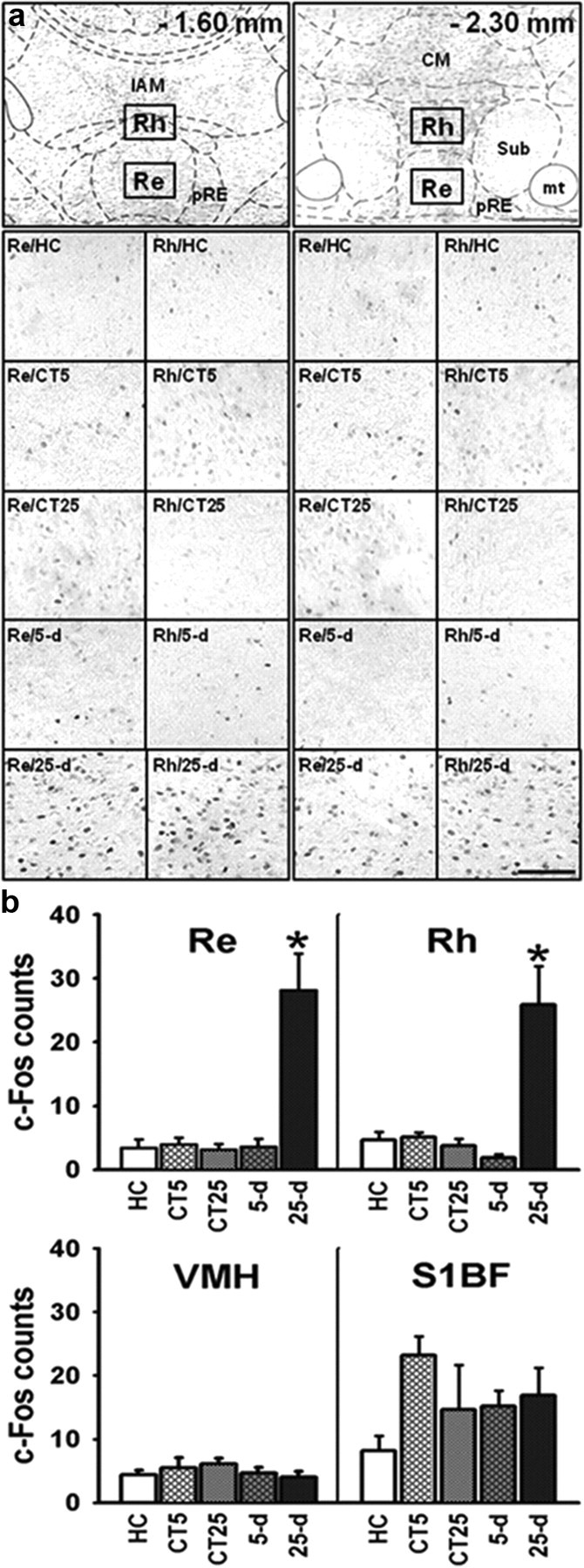
a, Coronal sections through the ventral midline thalamus and schematic delimitation of several nuclei therein according to Paxinos and Watson (1998) at two AP levels (top). Typical examples of c-Fos expression patterns in the Re and Rh are shown in the photographs (bottom; their location corresponding to the rectangles shown in the top) for the two control conditions (5 d, nHC = 3, nCT = 6; 25 d, nHC = 2, nCT = 5) and at the two postacquisition delays for rats trained with the hidden platform in the water maze (5 d, n5 d = 8; 25 d, n25 d = 7). CM, central medial thalamic nucleus; CT, curtain; HC, home cage; IAM, interanteromedial thalamic nucleus; mt, mammillothalamic tract; Re, reuniens nucleus; Rh, rhomboid nucleus; Sub, submedius nucleus; pRe, perireuniens; 5 d, 5-day postacquisition delay; 25 d, 25 d postacquisition delay. b, Quantification of c-Fos-positive nuclei in the two ventral midline thalamic nuclei (Re and Rh) and in two control structures, the VMH, and the primary somatosensory cortex (S1BF), under different control conditions (HC, CT5, and CT25) and after recent (5 d) or remote (25 d) memory retrieval in the rats trained with a hidden platform. Data are shown as the mean + SEM. Statistics: *p < 0.001 versus all other groups. A marked increase in c-Fos expression was noticed only in the Re and Rh and after retrieval of a remote spatial memory in the rats trained with the hidden platform as compared to all other groups (HC, CT at both delays, and recent memory). No such increase occurred in the two control structures, i.e., the VMH and S1BF.
