Figure 5.
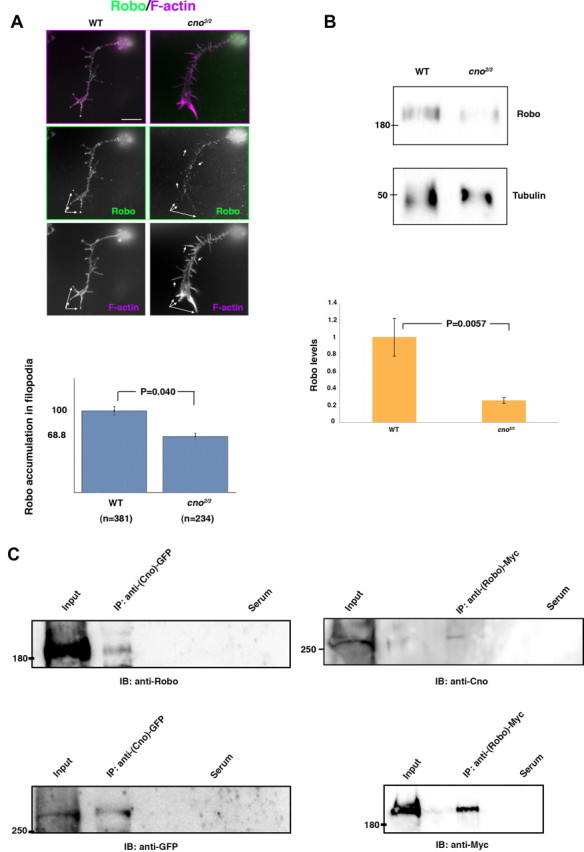
Cno forms a complex with Robo in vivo and regulates Robo subcellular localization in primary neurons. A, Primary neurons stained with anti-Robo (green) and phalloidin (F-actin, magenta). In cno2/2 mutant neurons, prominent Robo accumulations in filopodia (white arrows) are absent or decreased compared with WT neurons; quantifications are shown in the bar graph below (n, number of neurons analyzed). In each neuron, Robo dots per filopodia were counted and then averaged and normalized with respect to the WT. B, Western blots of cno2/2 mutant embryo extracts revealed a decrease in the overall amounts of Robo compared with WT embryo extracts (tubulin was used as loading control). C, Lysates of embryos expressing Cno-GFP or Robo-Myc were immunoprecipitated (IP) with rabbit anti-GFP or mouse anti-Myc and probed on immunoblots (IB) with anti-Robo or with anti-Cno (upper blots) and with anti-GFP or anti-Myc (as IP controls, lower blots). In negative controls (Serum), embryo lysates were immunoprecipitated with unspecific rabbit or mouse serum and treated under the same conditions. Scale bar, 5 μm.
