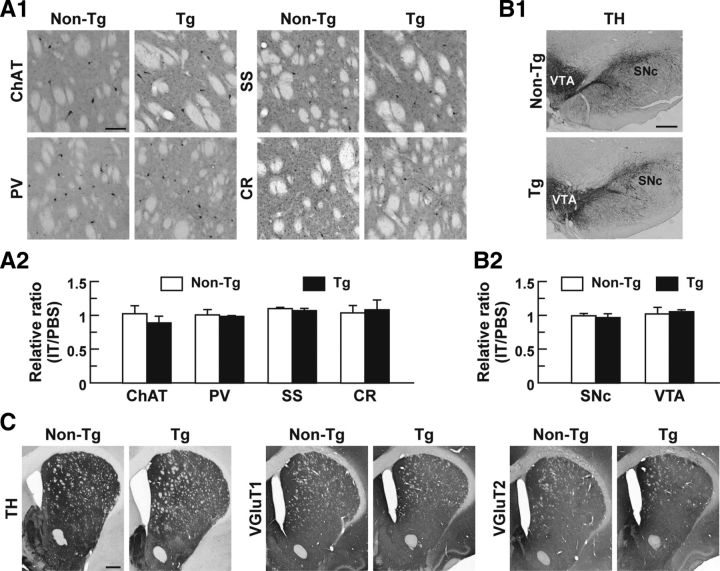
Figure 3.
Impact of IT injection on striatal interneuronal types, midbrain dopaminergic neurons, and synaptic terminals in the DLS. A, Localization of striatal interneuronal types. Sections through the dorsal striatum were stained immunohistochemically for specific markers of the interneurons, including choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) for cholinergic interneurons and parvalbumin (PV), somatostatin (SS), and calretinin (CR) for GABAergic interneurons. Light microscopic images of the DLS on the IT-injected side are shown (A1). Cell number ratios for the immunohistochemical images on the IT-injected side relative to the PBS-injected side were calculated (A2). n = 4 for each group. B, Morphology of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Sections through the ventral midbrain including the SNc and VTA were stained immunohistochemically for TH. Light microscopic images on the IT-injected side are shown (B1). Cell number ratios for the immunohistochemical images on the IT-injected side relative to the PBS-injected side were calculated (B2). n = 4 for each group. C, Distribution of dopaminergic and glutamatergic nerve fibers. Striatal sections were stained immunohistochemically for TH and vesicular glutamate transporters 1/2 (VGluT1/2) to visualize dopaminergic and glutamatergic fibers, respectively. Light microscopic images on the IT-injected side are presented. Scale bars: A, 100 μm; B, 400 μm; C, 1 mm.