Figure 4.
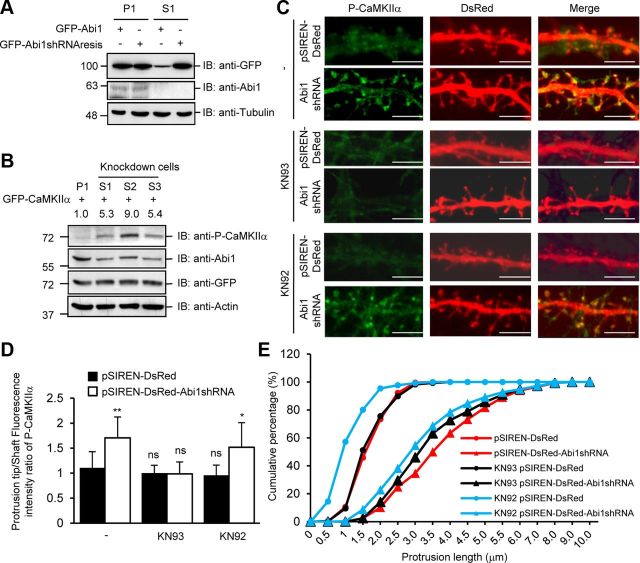
Knockdown of Abi1 in HeLa cells and rat hippocampal neurons elicit increased CaMKIIα autophosphorylation. A, HeLa cells stably expressing pSIREN-DsRed (P1) and pSIREN-DsRed Abi1shRNA (S1) were transfected with GFP-Abi1 or shRNA-resistant GFP-Abi1 (GFP-Abi1shRNAresis) and immunoblotted (IB) with indicated antibodies. Tubulin was used as the loading control. B, HeLa cells stably expressing pSIREN-Dsred (P1) and pSIREN-DsRed Abi1shRNA (S1, S2, and S3) were transfected with GFP-CaMKIIα. CaMKIIα autophosphorylation was examined by immunoblotting. Changes in P-CaMKIIα were quantified and expressed in arbitrary units as changes in P-CaMKIIα/GFP-CaMKIIα compared with control cells. C, 14 DIV neurons transfected with pSIREN-DsRed or p-SIREN-DsRed-Abi1shRNA (Abi1shRNA) were treated with or without 10 μm KN93 or 10 μm KN92. Representative neurites for each condition are shown. Scale bars, 5 μm. D, E, Results of subjecting 7310 dendritic protrusions from 120 neurons to morphometric analysis. Protrusion tip/shaft fluorescence intensity ratio of P-CaMKIIα in neurons was quantified for each condition (D). Compared with pSIREN-DsRed-transfected neurons, ratio of P-CaMKIIα increased in control and KN92-treated pSIREN-DsRed-Abi1shRNA neurons (mean ± SEM, *p = 0.001, **p < 0.00001; ns, not significant; Student's t test). Protrusion lengths were measured for each condition (E).