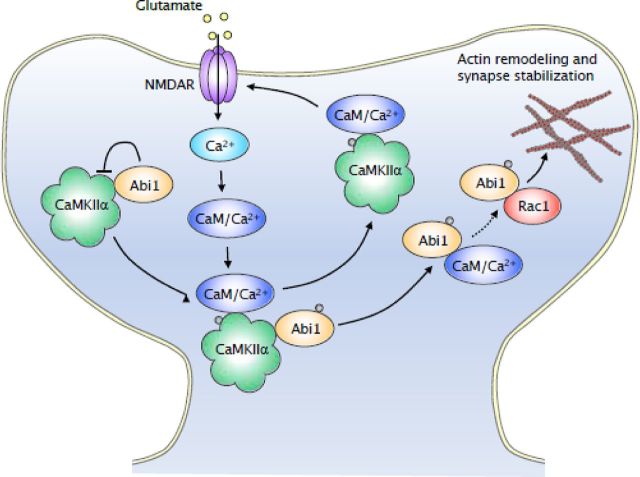
Figure 8.
Proposed model for the roles of activity-dependent interaction between Abi1 and CaMKIIα in spine regulation. At basal levels, Abi1 is bound to CaMKII and this interaction results in the mutual inhibition of their activity. Once glutamate receptors are activated, there is an increase in intracellular calcium, which induces Ca2+/CaM to trigger CaMKII activity. Active CaMKII phosphorylates Abi1 and binding of Ca2+/CaM to Abi1 elicits dissociation of Abi1 from CaMKII. Phosphorylated Abi1 then binds to Rac complex and activates Rac.