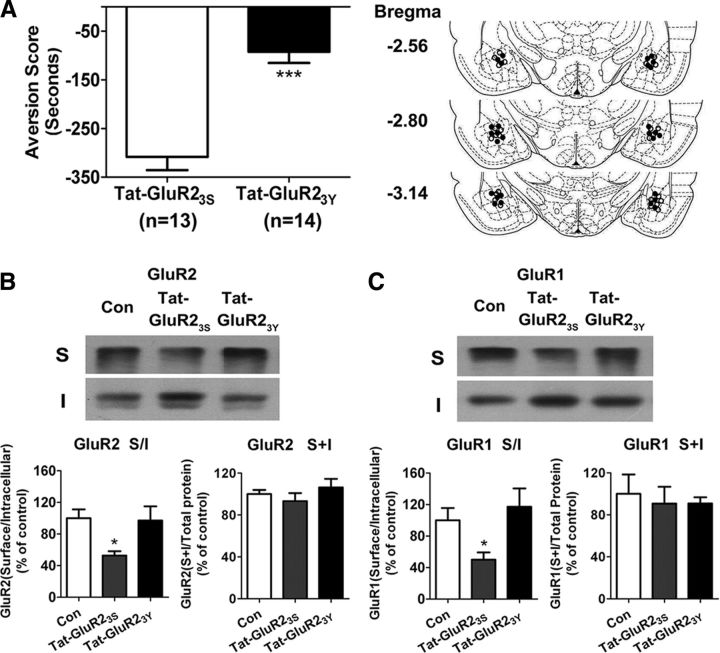
Figure 6.
Intra-amygdala injections of Tat-GluR23Y prevented the formation of conditioned place aversion and the endocytosis of GluR1- and GluR2-containing AMPARs induced by conditioned morphine withdrawal. A, Left, Bilateral microinjection of Tat-GluR23Y but not Tat-GluR23S into the amygdala blocked CPA formation induced by CMW; right, the image of schematic illustration of Tat-GluR23S and Tat-GluR23Y injection sites in the amygdala. ○, Tat-GluR23S injection; ●, Tat-GluR23Y injection. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, compared with the Tat-GluR23S-injected groups, two-tailed Student's t test. B, C, Tat-GluR23Y peptide prevented the endocytosis of GluR2- and GluR1-containing AMPARs induced by conditioned morphine withdrawal. Top panels show representative blots of surface (S) and internalized (I) GluR2- and GluR1-containing AMPARs from amygdalar tissues prepared from rats 1 h after conditioned morphine withdrawal. Bottom panels show quantification of surface/internal GluR2- and GluR1-containing AMPARs levels from Western blot data. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, compared with the corresponding saline-treated control group, one-way ANOVA with Newman–Keuls post hoc test.