Figure 7.
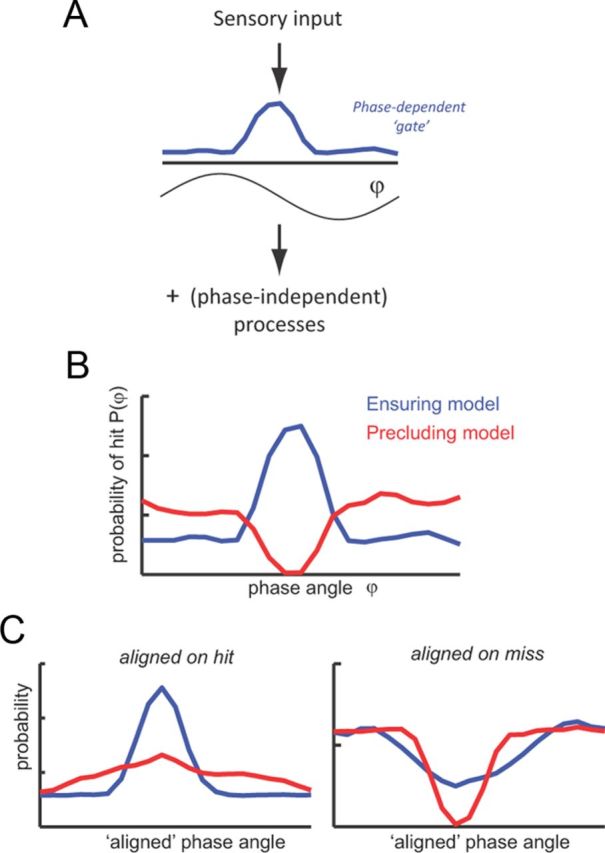
Conceptual model of ensuring and precluding roles of oscillation for auditory detection. A, Schematic of the model, which assumes that the chance for target detection P(φ) depends on a phase-dependent gating function and additional (phase-independent) processes. B, An ensuring role of oscillations is described by a gating function P(φ) that peaks for a specific phase range φopt and is flat otherwise. A precluding role is described by a detection probability that is especially low for a specific phase range φbad and flat otherwise. C, Subject-averaged hit rates were computed by assuming independent and uniformly distributed values of φopt and φbad. As the experimental data (see Fig. 3E), we calculated subject-averaged results by aligning individual subject data both on peak hit rates and peak miss rates. The ensuring model yields stronger modulation when aligned to hit (compared with aligned to miss), whereas the precluding model yields the opposite. The latter is consistent with our experimental data.
