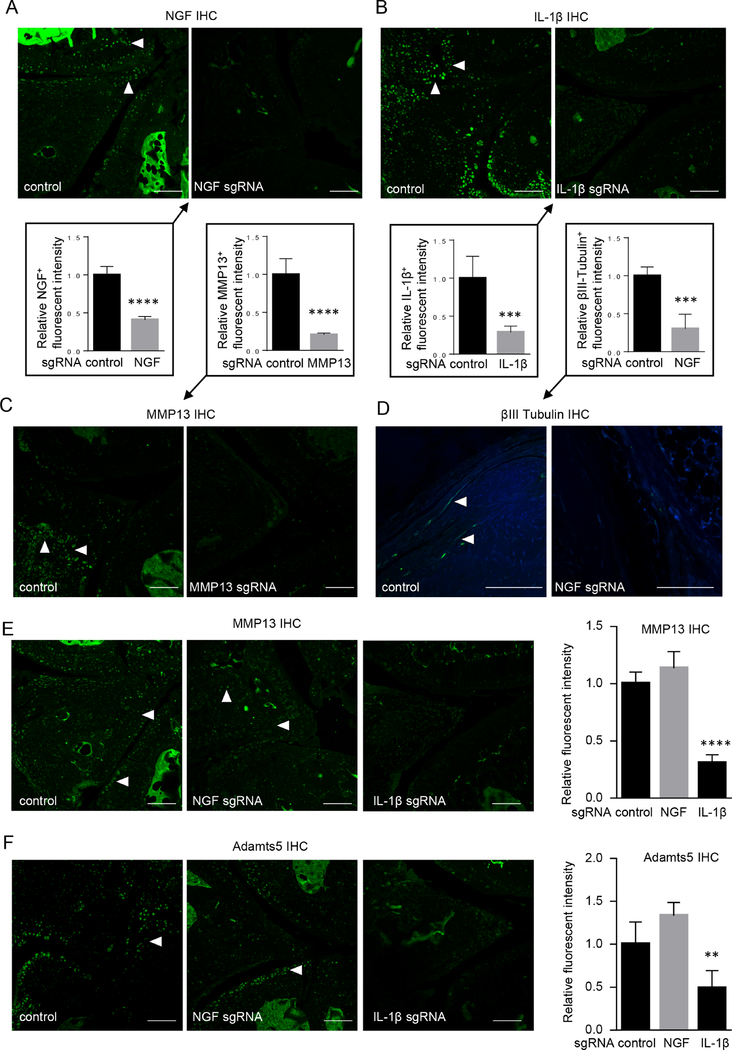
Figure 2.
CRISPR-mediated gene editing attenuated OA-associated downstream signalling. (A–C) Administration of gene-ablating AAV reduced the expression of the individual targets in osteoarthritic knee joints, such as NGF (A), IL-1β (B) and MMP13 (C). (D–F) NGF-targeting AAV downregulated the expression of βIII tubulin (D), MMP13 (E) and Adamts5 (F) and IL-1β-targeting AAV reduced the expression of MMP13 (E) and Adamts5 (F) in osteoarthritic knee joints. Arrowheads, IHC-positive cells. n=5. Scale bar, 50 μm. Unpaired Student’s t-test (A–D) or one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey-Kramer test (E,F). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. AAV, adeno-associated virus; ANOVA, analysis of variance; IHC, immunohistochemistry; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; MMP13, matrix metalloproteinase 13; NGF, nerve growth factor; OA, osteoarthritis.