Figure 5.
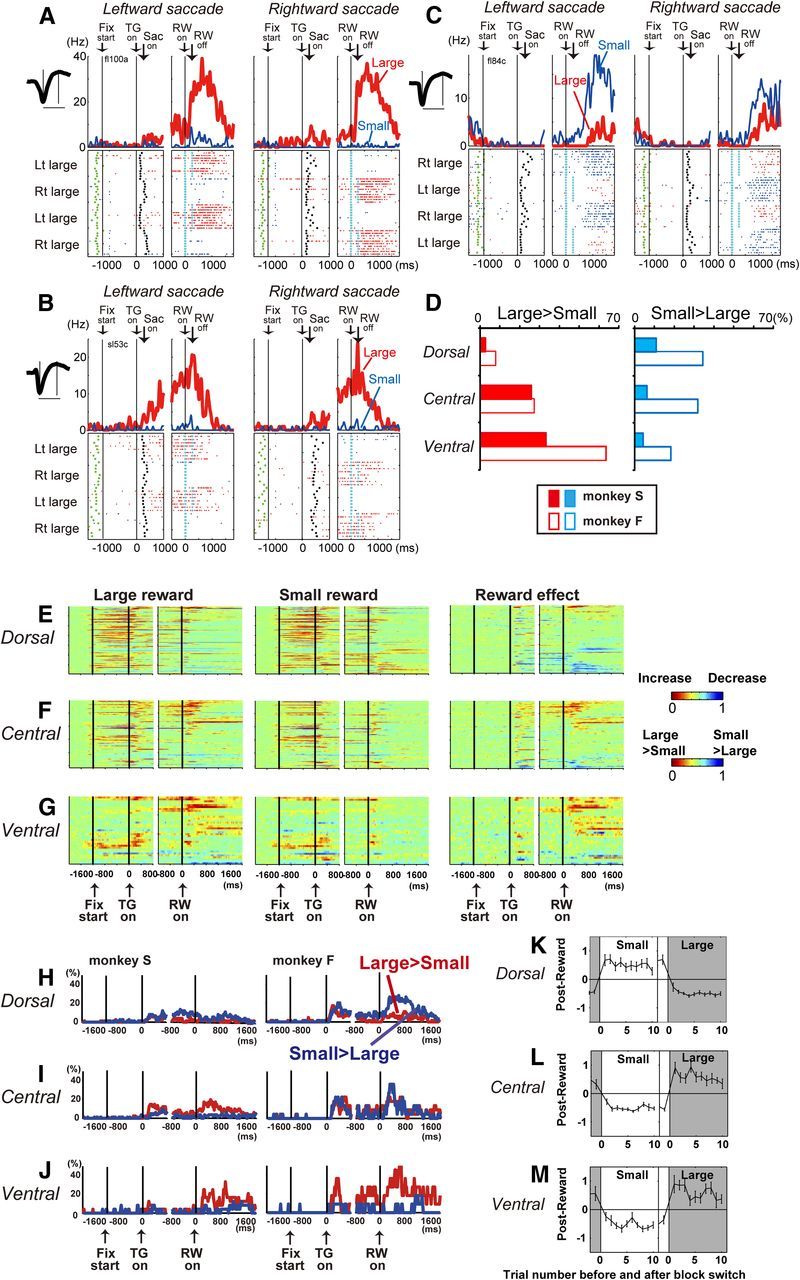
Reward size effect. A–C, Examples of ventral (A), central (B), and dorsal (C) caudate neuronal activity showing a reward-size effect. The layout is the same as in Figure 4A. D, Percentage of neurons that showed a significant reward-size effect. E–G, Temporal course of the reward-size effect of each neuron. Left and middle columns, Changes in neuronal firing rate from baseline are compared for large- and small-reward trials, separately. The color of each pixel indicates the ROC value based on the comparison of the firing rate between a control period just before fixation onset (400 ms duration) and a test window centered on the pixel (100 ms duration). This analysis was repeated by moving the test window in 20 ms steps. Warm colors (ROC > 0.5) indicate an increase in the firing rate relative to the control period, whereas cool colors (ROC < 0.5) indicate a decrease in the firing rate. Right column, Changes in reward-size-dependent modulation. The ROC value of each pixel was based on the comparison of the firing rate in the same test window centered on the pixel between the large- and small-reward trials. Warm colors (ROC > 0.5) indicate higher firing rates for large- than for small-reward trials, whereas cool colors (ROC < 0.5) indicate higher firing rates for small- than for large-reward trials. In all panels, the neurons have been sorted in order of their ROC values and the length of time with significant reward modulation during the post-reward (0–1600 ms) period. H–J, Temporal course of the fraction of neurons that showed a significant reward-size effect for each time bin (100 ms duration, two-way ANOVA, p < 0.01). K–M, Trial-by-trial changes in post-reward activity. Large-reward trials are indicated by the dark gray areas; small-reward trials are indicated by the white areas. Shown are the mean and SE of the normalized post-reward activity of the nth trial before and after contingency reversal: K, dorsal caudate neurons with small-reward preference (n = 26); L, central caudate neurons with large-reward preference (n = 24); M, ventral caudate neurons with large-reward preference (n = 16).
