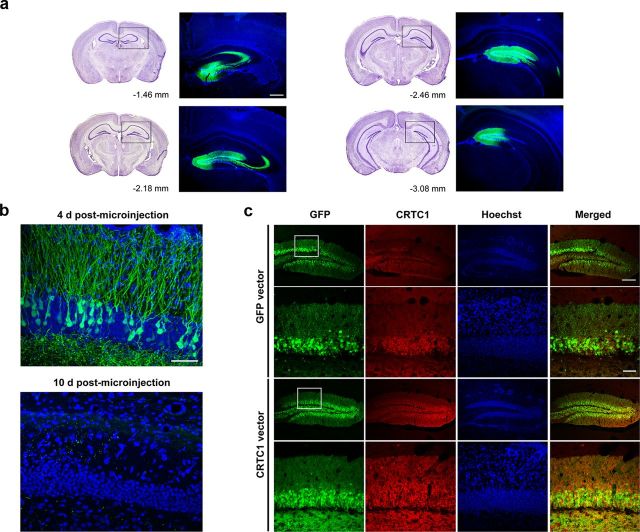
Figure 2.
Microinjection of CRTC1 vector induces robust expression of CRTC1 in the DG. a, Vector microinjection induces robust localized transgene expression (GFP, green) in DG of dorsal hippocampus. Left, Coronal brain images (adapted from Paxinos and Franklin, 2001) depicting the AP extent of typical viral vector infection (−1.46 to −3.08 mm posterior to bregma). Right, Corresponding image showing transgene expression (GFP, green) following vector microinjection (assessed 4 d postmicroinjection; counterstained with DAPI, blue). Scale bar, 200 μm. b, HSV preferentially infects excitatory neurons (DG granule cells) (assessed 4 d postmicroinjection, top; counterstained with DAPI, blue). Scale bar, 50 μm. HSV-driven transgene expression dissipates by 10 d postmicroinjection (bottom). c, Microinjection of CRTC1 vector increases CRTC1 protein levels. Immunohistochemical staining for CRTC1 protein (red) in the DG 4 d following microinjection of GFP vector (top) or CRTC1 vector (bottom). Mice microinjected with CRTC1 vector show higher levels of CRTC1 protein levels than mice microinjected with GFP vector, in infected neurons (green). Scale bars: 200 μm (top); 50 μm (bottom).