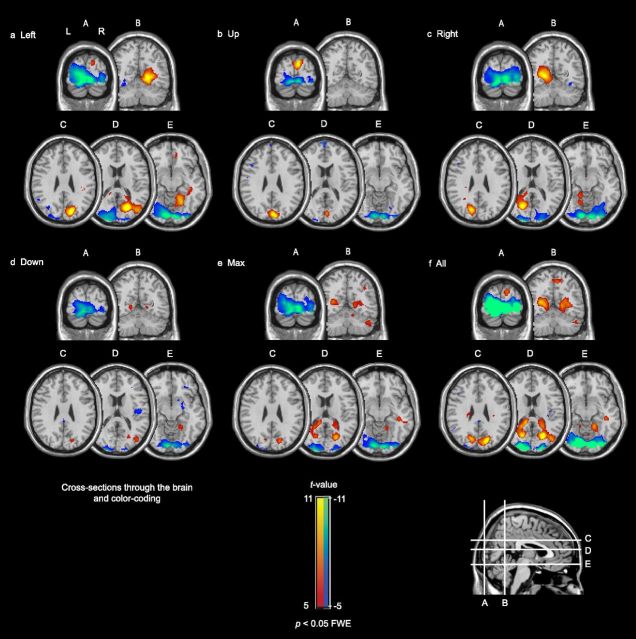
Figure 4.
Brain responses to the five peripheral gaze directions, contrasted with gazing straight ahead. The responses of tinnitus and control subjects were combined (n = 27). Deactivation was found in primary visual cortex (A–E); activation was found in precuneus (a, c–e; cross sections B–E), and dorsally in the occipital lobe (b; cross sections A, C). f, Shows the average activation and deactivation across all subjects and all gaze directions. The red-yellow color-code indicates areas with a significantly increased activity to gazing; the blue-green color-coded areas indicate areas with a significantly decreased activity.