Figure 5.
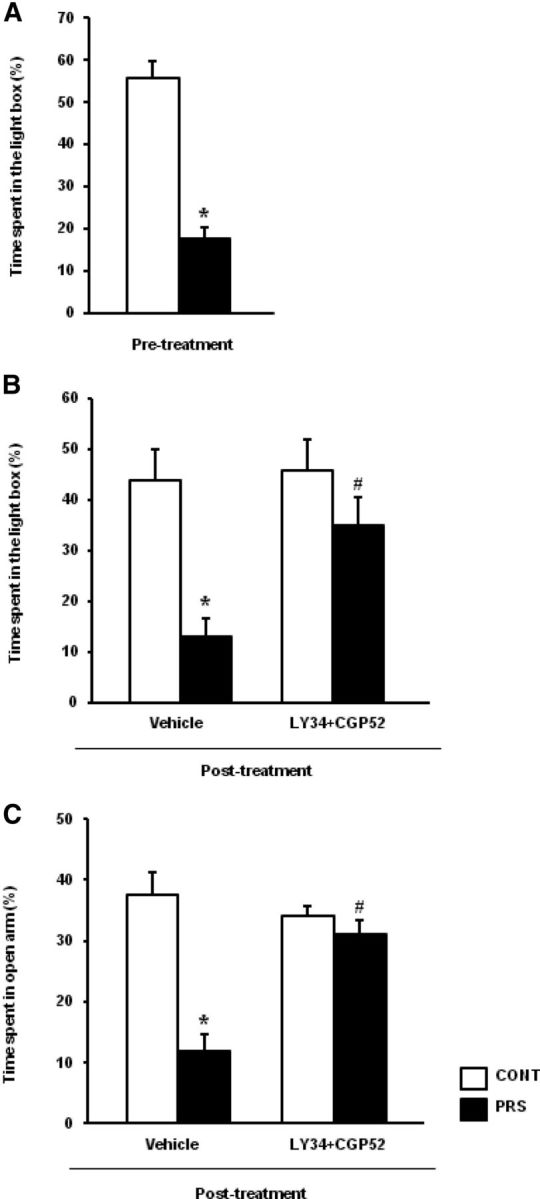
Pharmacological enhancement of glutamate release corrects anxiety-like behavior in PRS rats. All rats were tested in the light–dark box 1 week before surgery (i.e., 14–17 d before drug microinfusions in the ventral hippocampus). The time spent in the light compartment of the light–dark box in this pretest performed 14–17 d before is shown in A. Values are means ± SEM of 12 control (CONT) and 12 PRS rats. *p < 0.01 versus control rats. Behavioral data obtained in unstressed and PRS rats following microinfusion of vehicle or CGP52432 plus LY341495 in the ventral hippocampus are shown in B and C. Animals were first tested in the light–dark box and immediately after in the EPM. The effects of the first test experience might confound the interpretation of data of the second test (the EPM). However, the mixture of CGP52432 and LY341495 reduced anxiety-like behavior in PRS rats in both tests. The time spent in the open arm of the EPM and in the light compartment of the light–dark box in control and PRS rats bilaterally infused with 1 μl PBS containing 1 ng of CGP52432 and 100 pg of LY341495 or PBS alone (vehicle) in the ventral hippocampus are shown in B and C, respectively. Values are means ± SEM of six rats per group. p < 0.01 or p < 0.05 versus the respective control values (*) or versus the respective values treated with vehicle (#).
