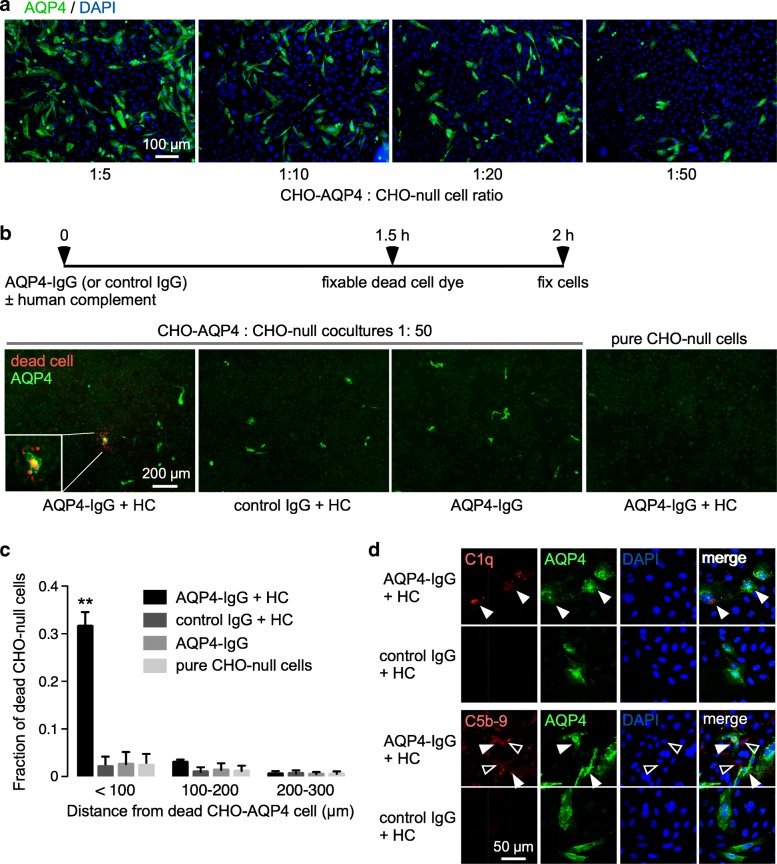
Fig. 1.
Complement bystander cytotoxicity in cocultures containing AQP4-expressing and null CHO cells. a AQP4 immunofluorescence (green) with DAPI counterstain (blue) in cocultures of CHO-AQP4 and CHO-null cells plated at different cell ratios. b Complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Cocultures at 1:50 cell ratio was incubated with 10 μg/ml AQP4-IgG (or control IgG) and 5% human complement (HC), with fixable red-fluorescent dead cell marker (left). AQP4 immunofluorescence (green) with dead cell stain (red) for cells incubated with AQP4-IgG and HC, with controls including cells incubated with control IgG and HC, with AQP4-IgG alone, and pure CHO-null cells incubated with AQP4-IgG and HC (right). c Fraction of red-stained dead CHO-null cells as a function of distance from dead CHO-AQP4 cells (mean ± S.E.M., 3 slides with > 50 dead cells analyzed, ** P<0.01 comparing AQP4-IgG + HC vs. control IgG + HC or AQP4-IgG or pure CHO-null cells by two-way ANOVA). d C1q (top) and C5b-9 (bottom) immunofluorescence (red) in cocultures incubated as in (b), costained with AQP4 (green) and DAPI (blue). White filled arrows indicate C5b-9 or C1q on CHO-AQP4 cells, white open arrows show C5b-9 on CHO-null cells