Figure 1.
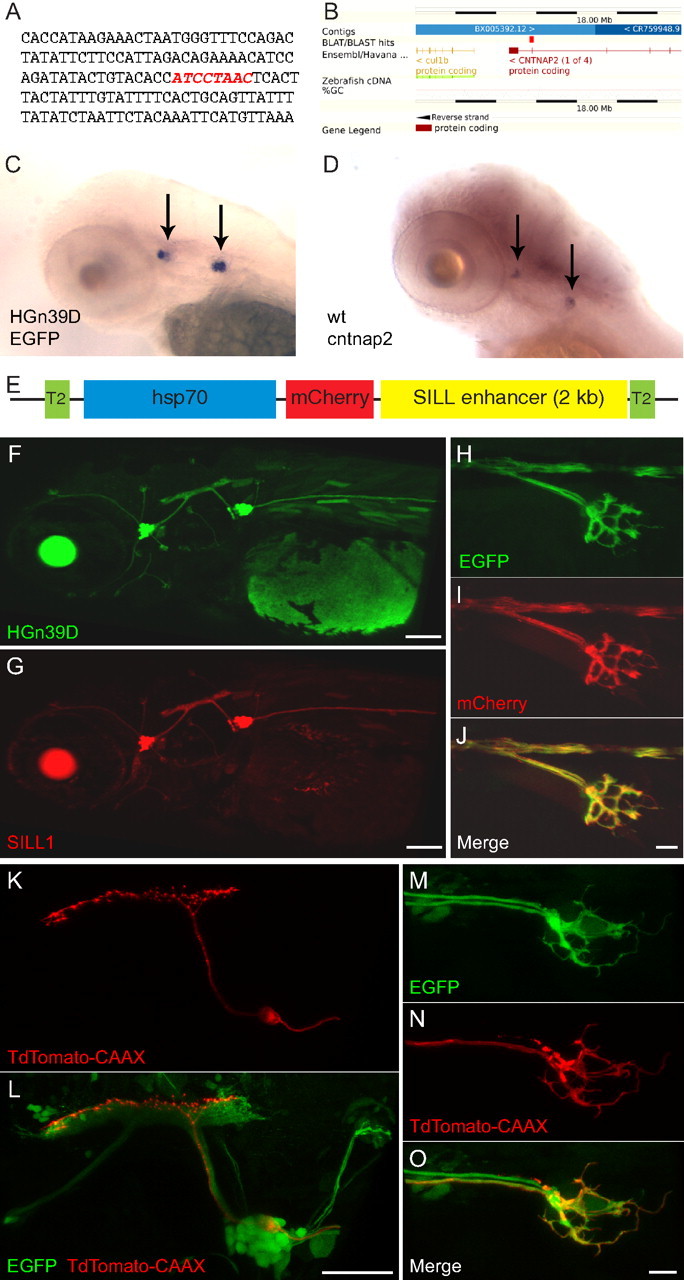
The SILL enhancer drives gene expression in the lateralis afferent neurons. A, The HGn39D enhancer-trap site indicated by red nucleotides. B, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) result shows the integration within Cntnap2a. C, D, Whole-mount in situ hybridization of the EGFP transcripts in 3 dpf HGn39D transgenic fish (C), and of the Cntnap2 transcripts in a wild-type specimen (D). Arrows indicate the anterior and posterior lateralis ganglia. E, Schematic representation of the SILL1 construct. F, G, Maximal projections of lateral views showing the expression pattern of EGFP in HGn39D (F) and of mCherry in Tg[SILL1] (G) at 3 dpf. H–J, Maximal projections of the peripheral axon arbor of Tg[HGn39D; SILL1] double transgenic fish at 3 dpf showing coexpression of EGFP (H) and mCherry (I). Merge is depicted in J. K, L, Maximal projections of the posterior lateralis ganglion and central axons showing TdTomato-CAAX (K) and EGPF (L) expression in a 5 dpf Tg[HGn39D; UAS:TdTomato-CAAX] double transgenic fish injected with the SILL2 construct that contains a Gal4-VP16 transcriptional activator. M–O, Tg[HGn39D; UAS:TdTomato-CAAX] double transgenic fish injected with the SILL2 construct expressing EGFP (M) and TdTomato-CAAX (N). Merge is depicted in (O). Scale bars: F, G, L, 100 μm; J, O, 10 μm. In all the panels and figures, dorsal is up and anterior is left.
