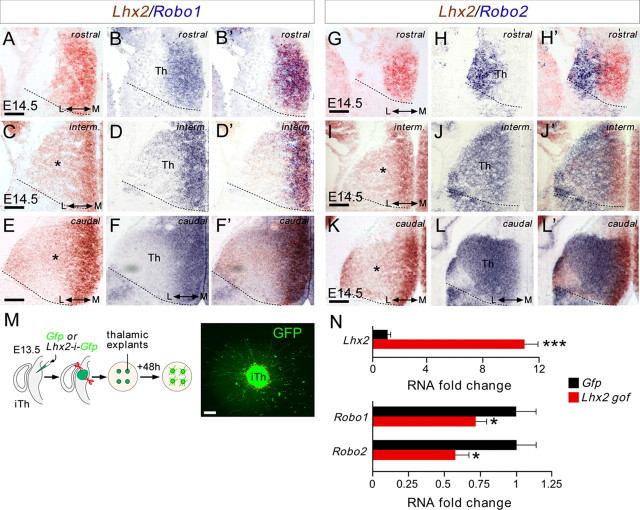
Figure 4.
Lhx2 represses Robo1 and Robo2 expression in thalamic-projecting neurons. A–L', Consecutive coronal cryostat sections at rostral, intermediate, and caudal thalamic levels of E14.5 wild-type embryos showing Lhx2 (A, C, E, G, I, K, red), Robo1 (B, D, F, blue), and Robo2 (H, J, L, blue) mRNA expression. The merged images are a composite of two consecutive sections for Lhx2 and Robo1 (B', D', F') or Robo2 (H', J', L') in situ hybridization. Asterisks highlight the Lhx2 gradients at the mRNA level. M, Schematic diagram of the experimental paradigm used for quantitative real-time PCR assays. E13.5 slices were electroporated focally with Egfp-coding or Lhx2-ires-Egfp-coding plasmids. Thalamic explants were dissected from the electroporated region and allowed to grow on coverslips coated with poly-l-lysine and laminin. N, Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of Robo1 and Robo2 expression in Egfp-electroporated and Lhx2-electroporated thalamic cells. Histograms show the fold change in RNA expression for Lhx2. Gene expression was normalized using GAPDH. Control conditions where normalized to 1 (±SEM). Asterisks indicate significance at *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001, Student's t test. Scale bars: A–L', 200 μm; M, 50 μm.