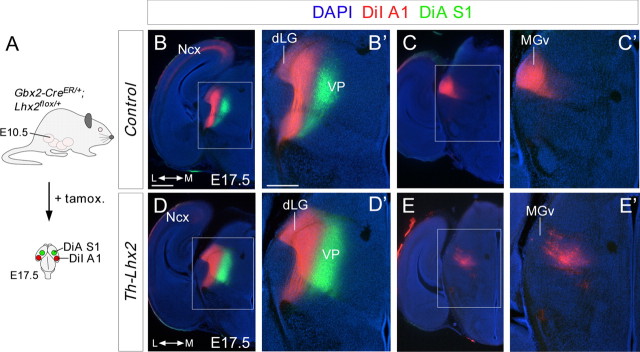
Figure 8.
Tracing experiments revealed topographical thalamocortical defects after the conditional deletion of Lhx2 in the thalamus. A, Schematic diagram illustrating the strategy used to conditionally delete Lhx2 by tamoxifen administration and the dye-tracing studies performed. B–E', Coronal sections showing retrograde-labeled cells in the distinct thalamic nuclei after DiI injection (red) into the A1 cortical area and DiA (green) into the S1 cortical area of control (B–C') and Th-Lhx2 (D–E') embryos. After injection in the A1, retrograde-labeled cells were observed in the dLG and MGv nuclei of control brains. However, no retrograde-labeled cells were observed in the MGv of Th-Lhx2 mice and abnormal retrograde labeling was observed in some ectopic thalamic neurons (E–E') in the most caudal part of the VP nucleus. Scale bars: (in B) B, C, D, E, 300 μm; (in B') B', C', D', E', 200 μm.