Figure 2.
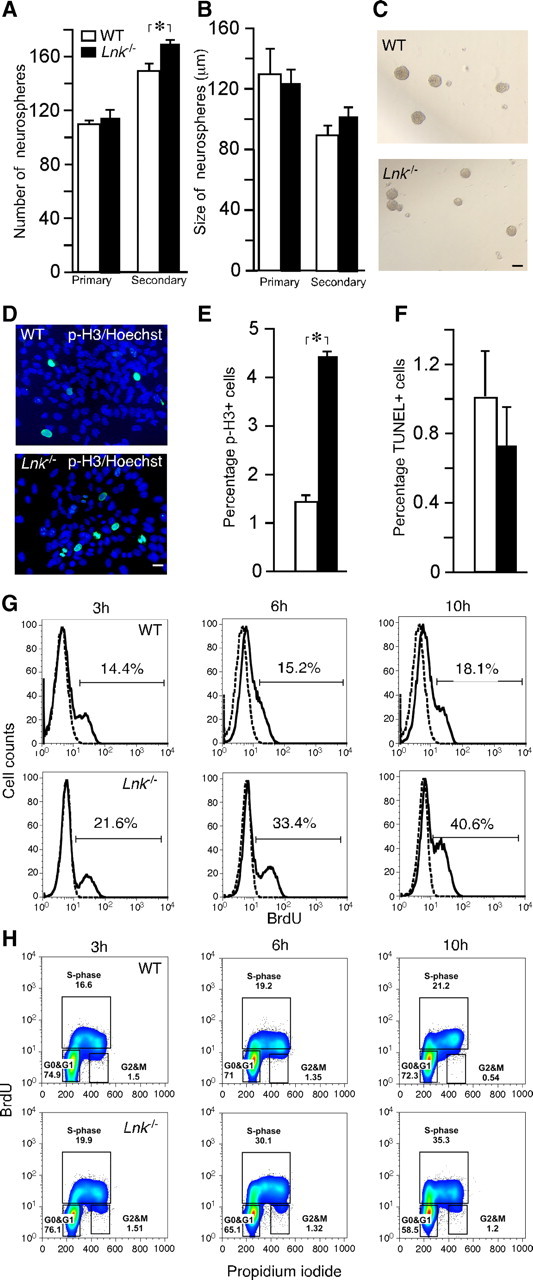
Deletion of Lnk leads to increased in vitro proliferation of SVZ NSPCs by shortening cell cycle duration. Number (A) and size (B) of primary and secondary neurospheres formed from WT and Lnk−/− SVZ. C, Photomicrographs of neurospheres from WT and Lnk−/− mice. Photomicrographs (D) and percentage of p-H3+ (E) and apoptotic TUNEL+ (F) neurosphere cells out of a total number of Hoechst+ cells. (G, H) FACS analysis of BrdU incorporation and cell cycle in WT and Lnk−/− NSPCs. Neurospheres were pulsed with BrdU and analyzed 3, 6, and 10 h thereafter. Histograms showing increased percentage of BrdU+ cells in Lnk−/− (bottom) as compared with WT (top) neurospheres (G). Bivariate (x-axis, propidium iodide; y-axis, BrdU) cell cycle distribution analysis of WT (top) and Lnk−/− neurosphere cells. Density plots showing increased percentage of cells in S- and G2/M-phase in Lnk−/− (bottom) as compared with WT (top) (H). Means ±S EM, n = 5 (A, B) and 4 (E, F). *p < 0.05, Student's unpaired t test. Scale bars: C, 100 μm; D, 10 μm.
