Figure 2.
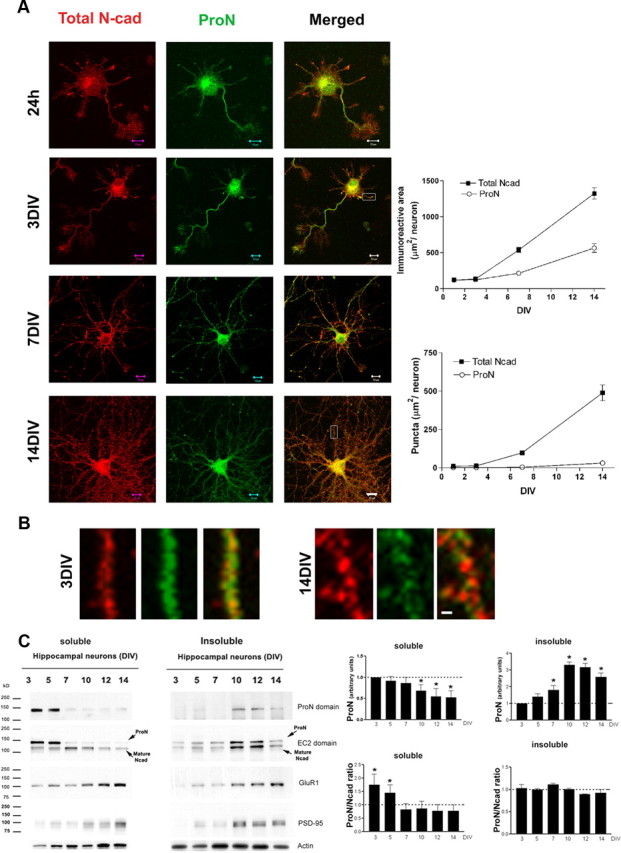
ProN versus total N-cadherin expression in hippocampal neurons. A, Primary hippocampal neurons stained for ProN (green) or total N-cad (red). At early stages of neuronal differentiation (3 DIV), ProN is highly expressed and the total N-cad pool consists mainly of ProN (quantified in the right panel). After 7 DIV, the relative contribution of ProN to the total N-cad pool drops considerably with simultaneous elevation in mature N-cad shown with a punctate distribution. B, ProN and total N-cad distribution shown at higher magnification. ProN distributes diffusely forming small puncta at 3 DIV. After 7 DIV, a high proportion of total N-cad distributes as larger puncta that fail to match with ProN labeling, demonstrating an increase in mature synaptic N-cad. C, ProN and N-cad distribution in detergent-soluble and -insoluble fractions. During differentiation, ProN and mature N-cad distribute from the detergent-soluble to the detergent-insoluble fraction. ProN is predominantly expressed in the detergent-soluble fraction at the early stages of neuronal differentiation (3–7 DIV), while mature N-cad mainly distributes into the detergent-insoluble fraction during synaptogenesis (7 DIV onward). From 7 DIV onward, both ProN and N-cad distribute into the detergent-insoluble fraction. Densitometry reveals that the ProN/N-cad ratio drops significantly only in the soluble fraction during neuronal differentiation. The ProN/N-cad ratio drops to ∼1 from 7 DIV onward, and constant levels are maintained that show no change in the detergent-soluble or -insoluble fractions. For comparison, expression levels and the distribution in the soluble and insoluble fractions of the synaptic proteins GluR1 and PSD-95 are also shown. The results are expressed as mean values ± SD (n = 4 independent cultures). Scale bars: A, 10 μm; B, 0.5 μm. *p < 0.001, compared with 7 DIV for the ProN/N-cad ratio in the soluble fraction or 3 DIV for ProN levels, by one-way ANOVA followed by Student–Newman–Keuls test.
