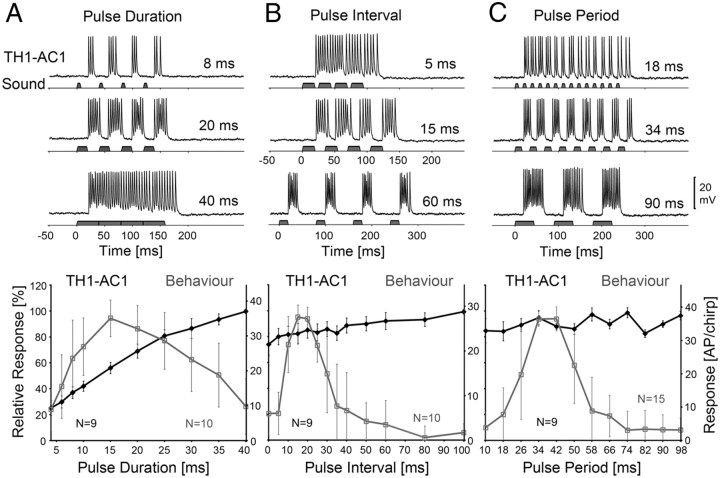
Figure 2.
Activity of TH1-AC1 and phonotactic tuning of female crickets to different PD, PI, and PP. A, Top, Response of TH1-AC1 at PD-8, 20, and 40 ms. Bottom, Phonotactic (gray) and neural (black) PD-response functions. B, Top, TH1-AC1 responses at PI-5, 15, and 60 ms. Bottom, Phonotactic (gray) and neural (black) PI-response functions. C, Top, Response of TH1-AC1 at PP-18, 34, and 90 ms. Bottom, Phonotactic (gray) and neural (black) PP-response functions. The left scale indicates relative neural and phonotactic activity, and the right scale shows the absolute values of spike activity. Neural data are based on N = 9 females and n = 54 test sequences; phonotactic data are based on N = 10 (A, B) and N = 15 (C) animals. Error bars show SD of relative values.