Figure 5.
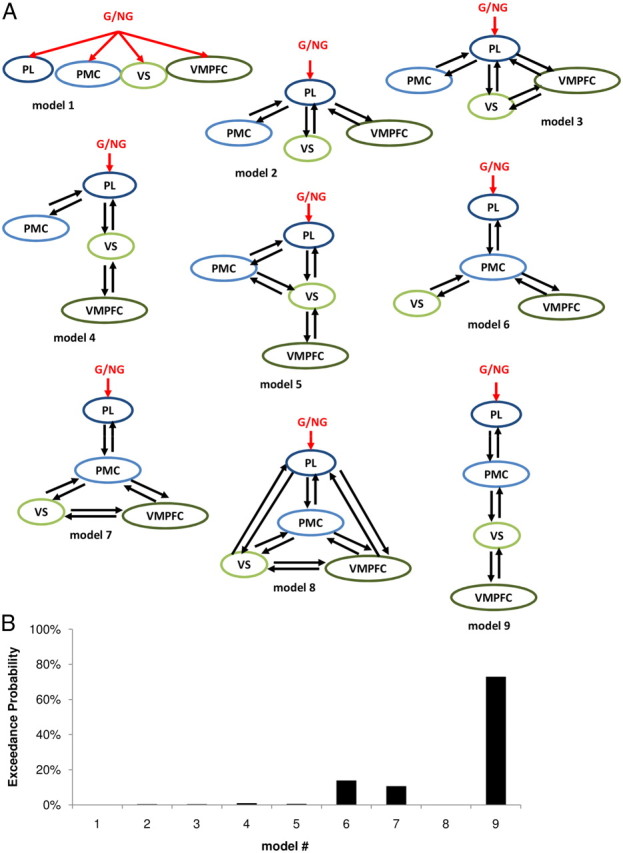
Network architecture. A, Illustration of alternative DCMs. In all models, the driving input (red) was a boxcar function over the video-viewing period, parametrically modulated by the experimental condition (1 for goal, 0 for nongoal objects). The different models account for different levels of branching, from a full parallel (model 1) to a serial caudorostral transfer of information (model 9). B, Results of the BMS procedure used to identify the most probable model.
