Figure 3.
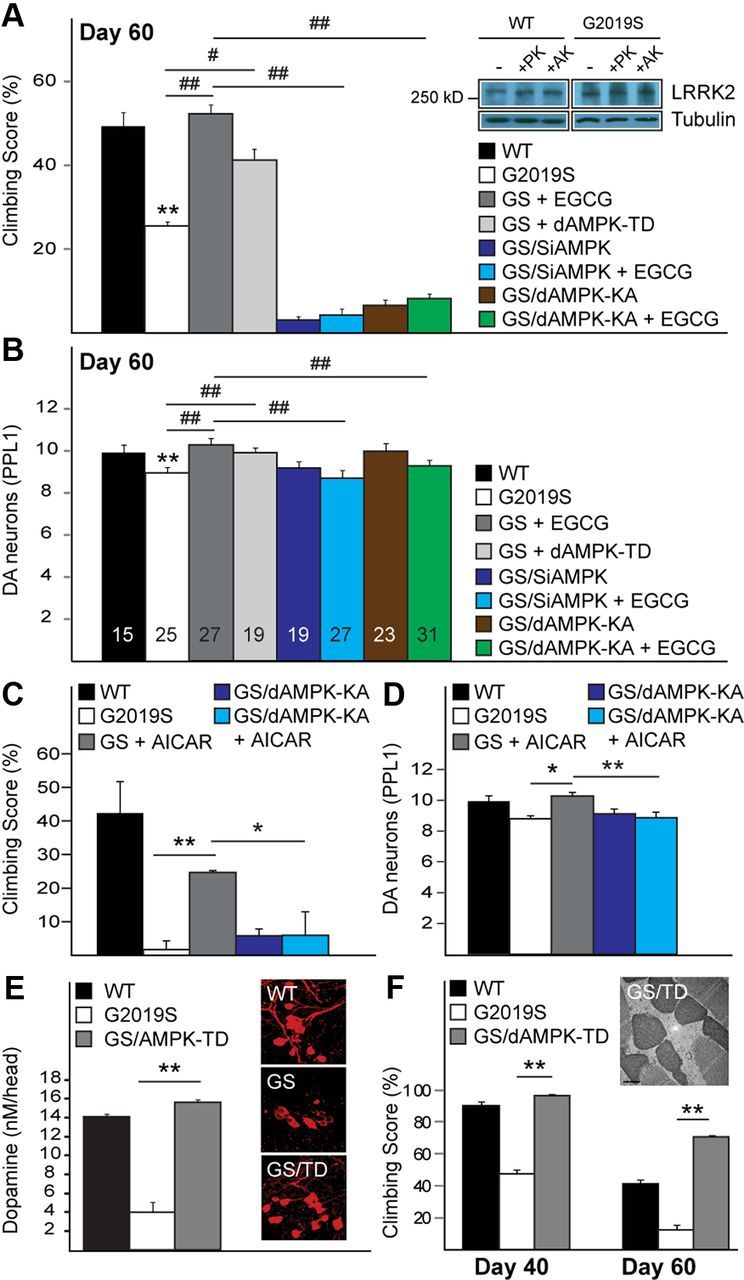
AMPK activation ameliorates Drosophila LRRK2 mutant phenotypes. A, B, Climbing score (A) and DA neuronal count (PPL1 cluster) (B) of untreated or EGCG-treated Ddc-driven G2019S LRRK2-expressing flies in the presence or absence of AMPK expression silencing (siAMPK), dominant-negative (dAMPK-KA), or constitutively active (dAMPK-TD) AMPK mutant, as indicated. Data for WT, G2019S, and G2019S + EGCG were derived from Figure 2, D and F. Inset, LRRK2 expression in the absence or presence of parkin (PK) or dAMPK (AK) coexpression (genotype: elav-Gal4-hLRRK2 or elav-Gal4-hLRRK2;elav-Gal4-hparkin or elav-Gal4-hLRRK2;elav-Gal4-dAMPK). Experiment was repeated at least three times with essentially similar results, C, D, Similar to A and B, except EGCG is replaced by AICAR. E, Dopamine levels in wild-type (WT) LRRK2, LRRK2 G2019S and LRRK2 G2019S/AMPK-TD flies as measured by HPLC. Inset, Confocal microscopy images of TH-positive neurons in PPL1 cluster of WT and G2019S (GS) LRRK2-expressing and G2019S/AMPK-TD (GS/TD) double-transgenic flies. F, Climbing score of 24B-driven G2019S LRRK2-expressing flies in the presence or absence of dAMPK-TD coexpression. Inset, Representative TEM image of indirect flight muscles of dAMPK-TD/G2019S double-transgenic flies (GS/dAMPK-TD).
