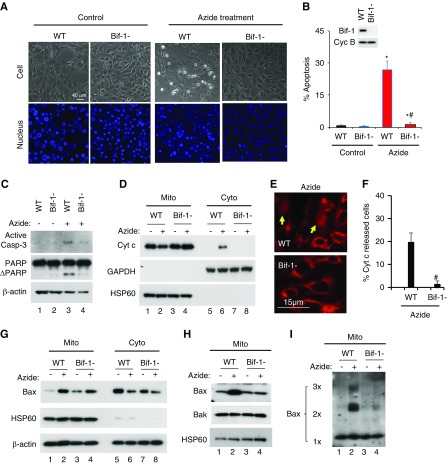
Figure 1.
Azide-induced intrinsic pathway of apoptosis is blocked in Bif-1-null MEF. (A–C) Apoptosis. WT and Bif-1-null MEFs were left untreated (Control) or treated with 20 mM azide in glucose-free buffer for 3 hours, followed by 2 hours of recovery in normal culture medium. The cells were then stained with Hoechst33342 to record cellular and nuclear morphology (A) and counted to determine the percentage of cells with apoptotic morphology (B), or were lysed for immunoblot analysis of active caspase 3, PARP, and cyclophilin B (loading control) (C). Insert in (B) is an immunoblot to confirm Bif-1 expression in WT MEFs and not in Bif-1-null cells. (D–F) Cyt c release from mitochondria. WT and Bif-1-null MEFs were treated with 20 mM azide in glucose-free buffer for 3 hours or left untreated. The cells were then fractionated into membrane-bound fraction with mitochondria (Mito) and cytosolic fraction (Cyto) for immunoblot analysis of indicated proteins (D), or fixed for immunofluorescence of Cyt c to record representative images (E) and count to determine the percentage of cells with Cyt c released into cytosol (F). Arrows in (E) point to the cells with Cyt c release. (G–I) Bax accumulation, insertion, and oligomerization in mitochondria. WT and Bif-1-null MEFs were treated with 20 mM azide in glucose-free buffer for 3 hours or left untreated. The cells were then fractionated into membrane-bound fraction with mitochondria (Mito) and cytosolic fraction (Cyto) for immunoblot analysis of indicated proteins (G). In addition, the Mito fraction was subjected to alkaline treatment to remove loosely attached proteins for immunoblot analysis of membrane-inserted Bax (H) or subjected to chemical crosslinking with 1 mM DSP for immunoblot analysis of Bax oligomerization (I). Immunoblots and images (A, C–E, G–I) are representatives of at least three independent experiments. The data (B and F) represent mean±SD (n=3; 300–600 cells evaluated per condition); *P<0.05 versus control; #P<0.05 versus WT/azide.