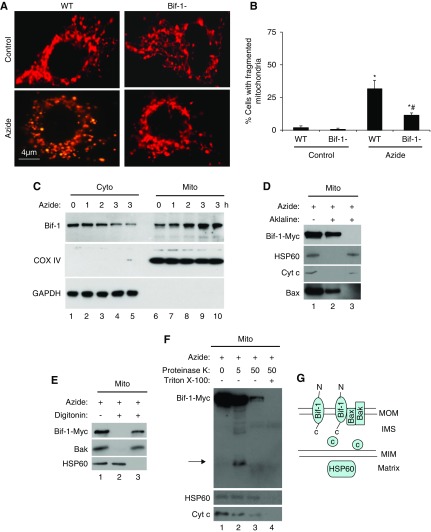
Figure 2.
Azide-induced mitochondrial fragmentation in apoptosis is attenuated in Bif-1-null MEF. (A and B) Lower mitochondrial fragmentation in Bif-1-null MEFs. WT and Bif-1-null MEFs were transfected with MitoRed to fluorescently label mitochondria, then incubated with 20 mM azide in glucose-free medium for 3 hours or left untreated. Representative images of mitochondrial morphology were recorded (A) and for quantification, the cells with fragmented mitochondria were counted to determine the percentage (B). The data in (B) represent mean±SD (n=3; >100 cells evaluated per condition); * P<0.05 versus control; #P<0.05 versus WT/azide. (C) Bif-1 translocation to mitochondria. WT MEFs were treated with 20 mM azide for 0–3 hours. The cells were then fractionated into membrane-bound fraction with mitochondria (Mito) and cytosolic fraction (Cyto) for immunoblot analysis of Bif-1. Cox IV and GAPDH were probed as cytosolic and mitochondrial markers. (D) Mitochondrial Bif-1 is resistant to alkaline stripping. HEK293 cells were transfected with Bif-1-Myc and treated with 20 mM azide for 2 hours to isolate mitochondria, which were incubated with alkaline (0.1 M Na2CO3, pH 11) buffer followed by centrifugation to collect pellet and supernatant fractions for immunoblot analysis of Bif-1-Myc, HSP60, Cyt c, and Bax. Whole mitochondria without alkaline incubation was analyzed as a control. The majority of Bif-1 remained on mitochondrial membranes after alkaline incubation. (E) Digitonin extracts Bif-1 from mitochondria. Isolated mitochondria were incubated with 0.5 mg/ml digitonin and then centrifuged to collect the soluble fraction (lane 3) and the pellet (lane 2) containing mitoplast. Nontreated mitochondria were used as a control (lane 1). Like Bak, Bif-1-Myc was solubilized by digitonin, whereas the matrix protein HSP60 remained in mitoplast. (F) Proteinase K protection assay. Isolated mitochondria were treated with 5 or 50 μg/ml proteinase K for 30 minutes on ice in the absence or presence of Triton X-100 (0.5%), and then centrifuged to collect pellet for immunoblot analysis. Without Triton X-100, 5 μg/ml proteinase K partially digested Bif-1, releasing a fragment that was detected by anti-Myc antibody (lane 2), whereas 50 μg/ml proteinase K induced more digestion, likely because of compromising the integrity of outer membrane (lane 3). In the presence of Triton X-100 (lane 4), all three proteins (Bif-1, HSP60, Cyt c) were degraded as a result of complete exposure to proteinase K. Arrow: Bif-1 fragment released after proteinase K digestion. (G) Schematic diagram of Bif-1 submitochondrial localization. Marker proteins from different compartments of mitochondria are also shown.