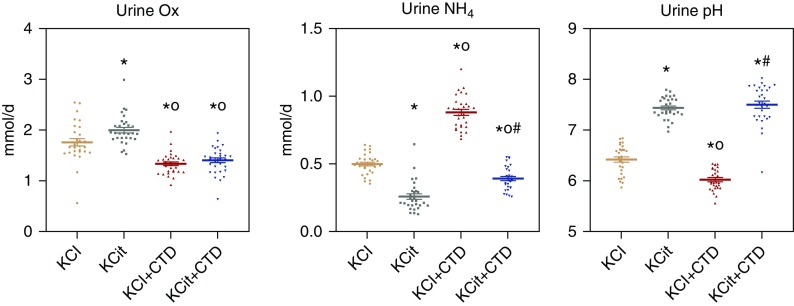
Figure 2.
Urine oxalate (Ox), NH4, and pH were significantly altered by KCit, CTD or KCit+CTD. Rat diets were supplemented with either potassium chloride (KCl; 4 mmol/d) as a control, KCit (4 mmol/d), CTD (1.25 mg/d) plus potassium chloride, or KCit+CTD. Twenty-four hour urine collections were done at 6, 12, and 18 weeks for analysis of solute levels as described in Methods and an overall mean of all three collections was calculated. Results are mean±SEM for ten rats per group. *P<0.05 versus potassium chloride; oP<0.05 versus KCit alone; #P<0.05 versus CTD alone.