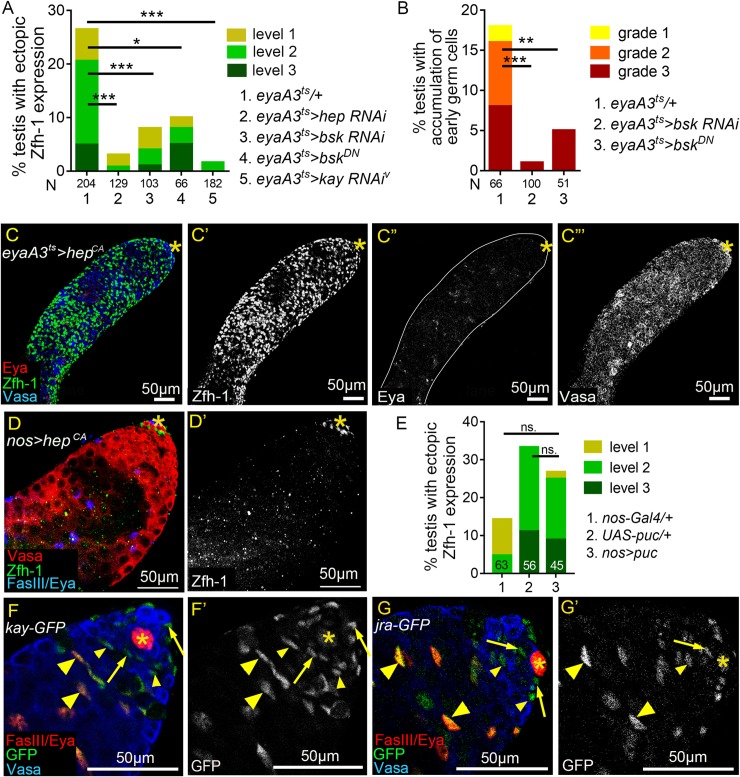
Fig 6. JNK signaling acts in cyst lineage to influence Zfh-1 expression.
(A and B) Reducing JNK signaling activity in cyst cell lineage suppressed reproduction-induced ectopic Zfh-1 expression (A) and expansion of early germ cells (B). N: number of testes scored. Animals were maintained at 25°C during development. (C-C”‘) 1w-old testis immunostained for Zfh-1 (green in C and white in C’), co-stained with Eya (red in C, and white in C”) and Vasa (blue in C and white in C”‘). Constitutive activation of JNK signaling led to massive accumulation of Zfh-1-positive cells (C), loss of Eya expression (C”), and block of spermatocyte differentiation (C”‘). (D and D’) 1w-old testis immunostained for Zfh-1 (green in D; white in D’), co-stained for Vasa (red in D), and Eya and FasIII (blue in D). Zfh-1 expression and germ cell differentiation appeared normal upon overexpression of HepCA in germ cells. Animals were maintained at 25°C during development. (E) Reduction of JNK signaling in germ cells by Puc overexpression did not suppress ectopic Zfh-1 expression in testes of mated 4w-old males. N = number of the testes scored. (F-G’) 1-3-day-old testes immunostained for GFP (green in F and G, and white in F’ and G’), co-stained for Vasa (blue in F and G), and for Eya and FasIII (red in F and G). Both Kay-GFP and Jra-GFP proteins expressed from the BAC genomic clones were detected in the nucleus of cyst cells, but not in the nucleus of germ cells. Arrows mark the CySCs, and small and large arrowheads indicate early and late cyst cells, respectively. P-values in A, B, and E are obtained by Chi-squared test. ns: p>0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001. Asterisks indicate the hubs. Mass-mating was conducted for experiments shown in A, B, and E.