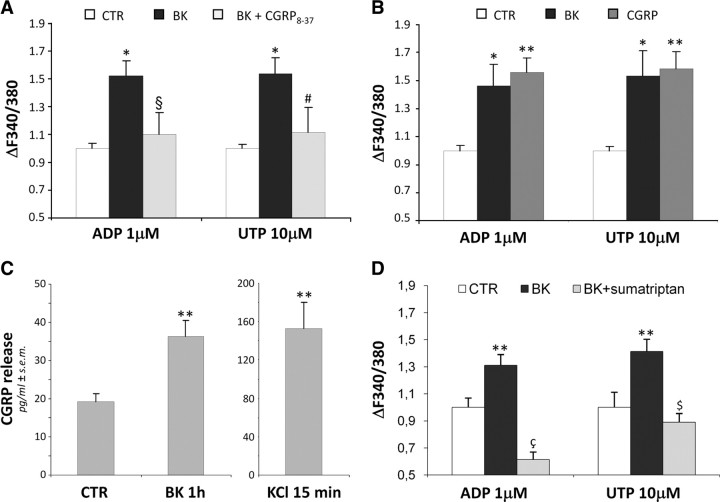
Figure 3.
BK-induced enhancement of P2Y receptor function in trigeminal SGCs is mediated by CGRP. A, Primary mixed trigeminal cultures were subchronically (24 h) treated with vehicle (CTR), or 100 nm BK alone and in the presence of the CGRP receptor antagonist CGRP8-37 (2 μm). Cultures were then challenged with 1 μm ADP or 10 μm UTP, and the increases in [Ca2+]i recorded from SGCs. *p < 0.05 with respect to CTR; §p < 0.05, and #p = 0.057 with respect to BK alone. B, Primary mixed trigeminal cultures were treated for 24 h with vehicle (CTR), 100 nm BK, or 1 μm CGRP, then exposed to ADP or UTP, and changes in [Ca2+]i analyzed in SGCs (see above). *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01 with respect to CTR. C, Histograms show the mean extracellular CGRP concentrations after 1 h application to primary mixed trigeminal cultures of either vehicle (CTR) or 100 nm BK. A 15 min exposure to 50 mm KCl was used as a positive control of maximal neuronal CGRP release. **p < 0.01 with respect to CTR. D, Primary mixed trigeminal cultures were treated for 24 h with vehicle (CTR) or 100 nm BK alone and in the presence of sumatriptan (10 μm). Cultures were then exposed to ADP or UTP, and changes in [Ca2+]i analyzed in SGCs (see above). **p < 0.01 with respect to CTR; çp < 0.01 with respect to both CTR and BK alone; $p < 0.01 with respect to BK alone. In A, B, and D, histograms show the mean [Ca2+]i normalized to CTR cells set to 1.0 from at least 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffé's test.