Figure 4.
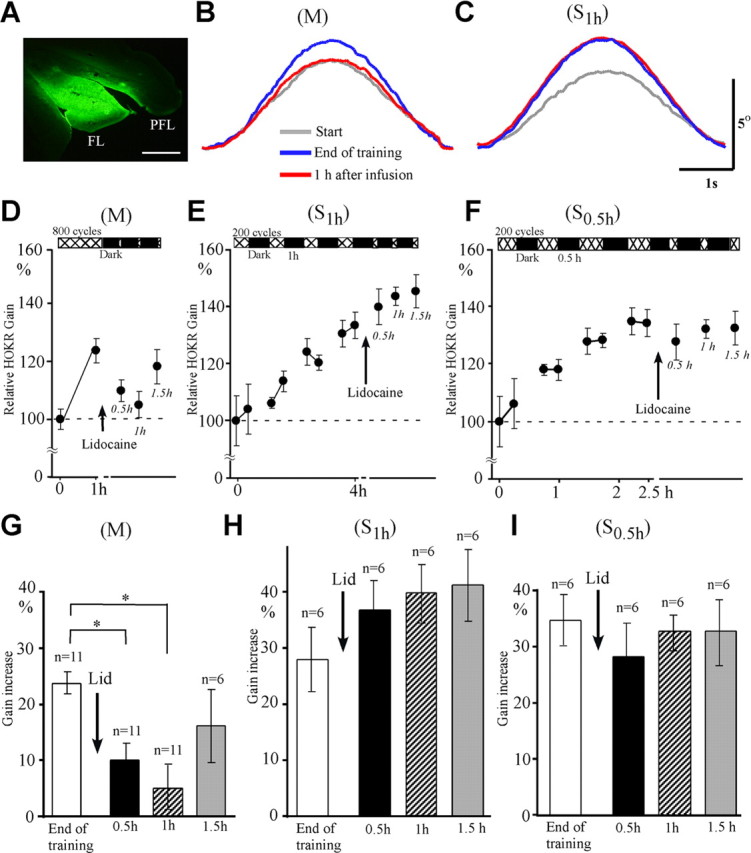
Effects of reversible shutdown of bilateral flocculi on adaptation induced by 800 cycles of massed training (M) and spaced training using 4 × 200 cycles at 1 h intervals (S1 h). A, Extension of lidocaine diffusion estimated by FITC infusion. FL, Flocculus. PFL, paraflocculus. Scale bar, 500 μm. B, Example of eye position traces before training (gray curve), at the end of training (blue curve), and 1 h after infusion of lidocaine (red curve) during M training. Averaged eye position traces from 16 to 25 cycles obtained from the same mouse are shown. C, Similar to B but for those during S1 h training. Averaged eye position traces from 16 to 27 cycles obtained from the same mouse are shown. Scale bars, 1 s and 5°. D–F, Time course of HOKR adaptation and effects of floccular lidocaine infusions for M (D), S1 h (E), and S0.5 h (F) training. G, Comparison of gain increase at the end of M training, 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h after lidocaine (Lid) infusions (n = 6–11). H, I, Similar to G but for those of S1 h training (H, n = 6) and S0.5 h training (I, n = 6). *p < 0.05 (Dunnett's test). Error bars indicate SE.
