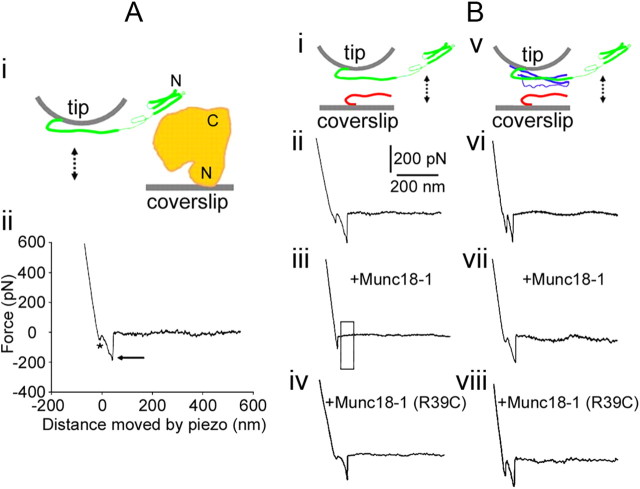
Figure 1.
Munc18-1 reduces the probability of interactions between Synt1A (green) and Syb2 (red) in the absence of SNAP25B (blue). Ai, The experimental approach. Recombinant full-length Munc18-1 (H6-Munc18-1; orange) is attached to the nickel-coated coverslip surface through H6 at its N terminus; the recombinant cytosolic tail Synt1A-H6 (green) is similarly attached by means of a C terminus histidine tag to the nickel-coated cantilever tip. These two proteins are brought into contact (approach; arrow pointing down) and then taken apart (retract, arrow pointing up). Aii, The retraction part of a typical force–distance (F-D) plot using a Synt1A-H6 functionalized tip and a H6-Munc18-1 functionalized coverslip. Asterisk indicates the segment of the plot while the coverslip and cantilever are still in contact; the arrow indicates the rupture of the protein–protein intermolecular bond. These two marks are omitted from the remaining F-D plots for clarity. Bi, Synt1A-H6 functionalized tips were used to probe Syb2–H6 functionalized coverslips (double arrow). Bii, The retraction part of a typical F-D plot showing interactions between Synt1A and Syb2. These interactions are absent when Munc18-1 is present in the recording solution (Biii; boxed area), but not in the presence of mutated Munc18-1 R39C protein (Biv). Bv, Synt1A-H6+H6-SNAP25B co-functionalized tips were used to probe Syb2–H6 functionalized coverslips (double arrow). Bvi, The retraction part of a typical F-D plot showing interactions between the proteins of the ternary SNARE complex. Bvii, Bviii, These interactions were unaffected by the presence of Munc18-1 (Bvii) or its R39C mutated form (Bviii). Drawings are not to scale. Position of Munc18-1 is arbitrary, as well as is the display of Synt1A in “ajar” form.